Category Archives: Specific Topics
(6) Treatment of pediatric chronic hepatitis
| Treatment of pediatric hepatitis is not difficult and treatment with the combination of TCM and WM is the most ideal. According to the principle of “treating the superficial when acute, and treating the fundamental when the onset is gradual,” for acute icteric hepatitis and severe cases of hepatitis, hospitalization is required. If treatment is administered with the combination of TCM and WM method, the effort used is lessened and also the course of disease is shortened. For chronic active and chronic persisting pediatric hepatitis, treatment with combined TCM and WM therapy is effective and safe. Physicians, experienced in TCM practice, are also capable of using TCM drugs to give their chronic hepatitis patients clinical cure.
A great amount of experiences have been accumulated in the treatment of liver disease with TCM. Although the TCM formulas are numerous, but basically, they concentrate into the following principles:
The representative formula, Yinchenhao Tang with addition and subtraction, is one used commonly in clinical practice with good results. Application of this formula (one parcel daily) usually alleviated clinical symptoms and causes retraction of the enlarged liver. When the liver is normal (lower margin of liver 1.5 cm above costal margin in percussion), continuation of the TCM therapy for 4-6 weeks cam eliminate the wetness-heat inside the body. Treatment is stopped at the attainment of clinical cure.
In the course of application of TCM formulas according to the child’s constitution, one can add or cancel some drugs in the formula. Experience in clinical application indicates that if the diagnosis is correct, no matter the symptoms belong to respiratory system or digestive system, there is no need to use too many TCM or WM drugs to deal with the symptoms. The symptoms from different systems caused by hepatophilic virus can similarly be eliminated rapidly.
Help children to take TCM drugs is not a hard job
Many people think that children are difficult to accept TCM drugs because of its bitterness. But, in fact, there is absolutely nothing to be afraid of, because human beings can gradually get accustomed to taste. Numerous clinical cases prove that after several trials of administration, children can gradually take the medicine by themselves. In some cases, we can add some sugar beforehand to correct the taste. For the avoidance of vomiting and lowering of drug effect, one can divide the drug taking into several times until the child is accustomed.
Tips for the Prevention of re-infection
It should be noticed that experience from numerous clinical cases indicated that clinical cure in children suffering from chronic hepatophilic virus disease can be obtained only by systemic therapy. But after clinical cure, children must be taught to conform to personal hygiene habits because it is only when stress put on personal hygiene that prevention of relapse of disease is possible. Some children suffering from repeated attacks of hepatomegaly should be put under consideration whether they have or not close contact with family members who are carriers of hepatitis virus or they are or not in a virus contaminated environment or whether their food are in a sanitary control or not. If the possible source of infection is detected, the change of some insanitary habits or avoidance of contact with hepatitis virus may be effective in the prevention or re-infection.
Be cautious about the following:
|
| By WONG Kwok Hung in 2003
translated by Professor ZHENG Hua En in July 2005 |
(5) Prognosis of pediatric chronic hepatitis
| The prognosis of pediatric virus hepatitis in general is better than adults, chiefly because the blood circulating in the liver of children is more than adults and also the genesis of liver cells is greater in children. But children with chronic active hepatitis are prone to develop cirrhosis of liver and carriers of type B hepatitis virus following infection by mother-infant communication are difficult to change into negative, so that a persisting positive condition is formed.
In pediatric hepatitis, because there is lowering of immune ability and digestive tract function, the patient is very susceptible to respiratory tract infection, such as pharyngitis, trachitis, tonsilitis and intestinal tract infection. In the convalescent stage, some patients may have the complications of fatty liver and secondary obesity. Some may be complicated by aplastic anemia, hemolysis and nephritis.
If systemic therapy is not obtained during childhood, then, in the after years of life, the patient would suffer from diseases of different systems under the control of hepatitis virus. Therefore, if in childhood, symptoms related to chronic hepatitis are not cured for a long time, one should remember to investigate the possibility of chronic hepatitis and give the patient TCM therapy to achieve clinical cure and stop the progression of the disease.
|
| By WONG Kwok Hung in December 2003
translated by Professor ZHENG Hua En in July 2005 |
4 Classification of forms in pediatric chronic virus hepatitis
| Virus hepatitis is a generalized disease; people of different constitution may have symptoms of different degrees from various systems. In pediatric virus hepatitis, all of the patient’s organs are directly or indirectly affected by hepatitis virus in the infantile stage or during childhood. In the course of disease immunocomplex (antigen-antibody complex) is formed and deposited in lymph nodes, spleen, vascular endothelium, renal glomerular basement membrane, synovial membrane and choroids plexus tissues where they produce inflammatory and degenerative changes.
According to the course of disease, liver function, immune status and pathologic changes, chronic hepatitis can be divided into “chronic persisting hepatitis” (CPH) and “chronic active hepatitis” (CAH). The former is due to the child’s weak immunologic function and inability to eliminate the hepatitis virus so that the disease is prolonged and cannot be cured; the latter is due to the child’s immunologic defect and insufficient antibodies and inability to eliminate the virus and to inhibit its replication. Furthermore, there are some liver cells, under the action of hypersensitized lymphatic cells being continuously destroyed, so that the disease persists, causing damage of multiple systems and appearance of different clinical symptoms.
Besides chronic hepatitis or acute anicteric hepatitis, subclinically infected patients and patients with occult infection can be all manifest mild, insignificant symptoms or even, may be asymptomatic. But if we can establish the diagnosis of virus hepatitis early enough, the pediatric patient would certainly be treated in time.
|
|
Classification of pediatric chronic hepatitis The clinical symptoms of pediatric hepatitis are summarized into the following forms for the purpose of better understanding and handling of these symptoms. Typical cases are introduced after each form, serving as references in clinical practice.
The 1st form – Lung dryness form The 2nd form – Gastrointestinal, dermal or lower jiao wetness-heat form The 3rd form – Nutritional disturbance or anemic form The 4th form – Endocrine disorder form The 5th form – Hypersensitive constitution form
|
|
By WONG Kwok Hung translated by Professor ZHENG Hua En in July 2005 |
(3) Recognization of the danger from hepatophilic virus
|
In the past, it was considered that only those which could induce clinical manifestations of hepatitis were ascertained as hepatitis virus. The latter is known, at the present time, to include seven types. In fact, besides hepatitis virus, many other viruses can also produce hepatitis and possess “hepatophilic” characteristics; these are the parotitis virus, simple herpes virus, cytomegalovirus, EB virus, Coxsackie virus, ECHO virus, yellow fever virus, German measles virus. These viruses have their respective clinical features, so they do not belong to the hepatitis virus group, but should be called in general “hepatophilic virus”.
Although these viruses are not called hepatitis virus but it does not mean that they do not induce hepatic infection (acute or chronic) of the host, leading to hepatomegaly and, at the same time, to hepatitis symptoms and extrahepatic manifestation and complications. Therefore, if clinical diagnosis is made on the basis of the past standard, large amounts of early and mild cases as well as cases with extrahepatic symptoms as chief manifestation would lose the chance of early treatment. In other words, “hepatophilic virus” should include several types of hepatitis virus and all related viruses that can cause symptoms of hepatitis. “Hepatophilic virus disease” should refer to patients with abnormal margin of liver dullness and with prolonged, repeated disease course indicating damage of multiple systems. These manifestations are the various clinical diseases caused by liver function damage.
Chronic hepatophilic virus disease is clinically a very common and typical virus disease. These viruses can evoke hepatitis after entering the human body. In spite of occultation of the virus and chronicity of the infection causing the induced clinical symptoms atypical and, therefore, often being neglected, yet the immune response of the body increases day by day. The latter condition promotes revelation of clinical symptoms and eventually leads to “hepatomegaly” which is a long lasting sign. This sign is the best object for the clinician to judge the effectiveness of therapy.
|
| By WONG Kwok Hung
translated by Professor ZHENG Hua En in July 2005 |
(2) The pathway of dissemination of pediatric chronic hepatitis
|
The pathway and mode of infection of virus hepatitis
Virus hepatitis is a common pediatric infection disease, the incidence, acute or severe cases and mortality of which are higher than those of adults. We may first look at the different pathways and mode of infection of different types of hepatitis virus so as to understand the dissemination and seriousness of pediatric hepatitis and to pay greater attention to gain more knowledge on our children’s health, to the early detection and treatment of the disease and to avoid their prolonged suffering from the attack of hepatophilic virus. In this way, the quality of health of the next generation can be improved and the effort used would be much less.
The “coaecrvation phenomenon” in virus hepatitis transmission
In virus hepatitis, the type most concerned is hepatitis B, because if the mother is a virus carrier, she may transmit the virus to the newborn. If the maternal blood is examined to be HBeAg positive (hepatitis B nuclear antigen positive), the chance of infection in the infant is 90% or more; but if HBe antibody positive (hepatitis B antibody positive), the chance of infection in the infant is comparatively small, usually 10% -15%.
Besides mother-child transmission, hepatitis B can also be transmitted through close contact between family members, and teeth brushing, use of bathing brush and razor blades in daily life can also transmit hepatitis B virus infection. Transmission through saliva and blood should be considered also as an important pathway of infection, because 30%-50% of chronic hepatitis B patients’ saliva show HBsAg (hepatitis B surface antigen) and attention should also be paid to spread by female menstrual blood. Therefore, to decrease the chance of dissemination, it is important to request good daily life habits, not to feed infants with chewed food, proper disposal of menstrual blood pollutant, washing hands before feeding and tableware sanitizing. It is only through these measures that family hepatitis virus infection, the “coacervation phenomenon” (a number of individuals in one family attacked by virus infection) can be prevented.
Clinical symptoms of pediatric hepatitis easily neglected
There is great difference in symptoms between mild and severe cases of virus hepatitis. In severe cases, the onset is acute, for example, in acute icterohepatitis, after the latent period, there is fever, fatigue, sleepiness, generalized tiredness, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation or common cold symptoms. About 2-8 days later, there is appearance of marked yellowish urine, the color similar to black tea or even sauce and it is then followed by jaundice of the sclera and skin, hepatomegaly, percussion tenderness of hepatic region or even telangiectasis of face, vascular spider and liver palm. The disease is not easy to be misdiagnosed because of the presence of jaundice, so the patient is usually discovered in time, isolated and treated accordingly.
But the anicteric type of hepatitis does not have jaundice, therefore, its symptoms may be mistaken as other virus diseases, such as common cold, influenza, upper respiratory tract infection, tonsillitis, trachitis and acute gastroentiritis. In fact, anicteric hepatitis has a higher incidence than the icteric type. As to the proportion of the clinical type to the non-clinical type, it is estimated to be 1 : 40, that is in 40 individuals with virus hepatitis, only one presents obvious symptoms. This condition reveals the popularity of hepatitis virus infection and that it is very easy to be neglected and misdiagnosed. Therefore, it should be noticed that the non-clinical typeincludes sub-clinically infected patients carrying hepatitis surface antigens but without symptoms. Attention should also be paid to latently infected patients carrying hepatitis antigens but without symptoms and chronic active hepatitis, chronic persisting hepatitis patients. If these pediatric patients are not discovered, they would not receive adequate treatment, their health and development would be impaired and the body constitution of the next generation is directly affected. Therefore, the first thing is to increase alertness on infections by hepatitis virus. If a direct relative or any person in close contact with the child has a history of acute or chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis or carcinoma of liver, or whose blood examination proves to be “antigen carrier” of hepatitis virus, or has abnormality of liver function, it should lead one to consider that the child has already been infected.
|
| Types of virus hepatitis
Recognize the danger of hepatophilic virus………
|
|
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A spreads all over the world; the places with high incidence include southeastern Asia, Africa, South America and China. 80% of newborn infants receive hepatitis A antibodies from the maternal placental circulation. But these antibodies mostly disappear in two years and infants have very high susceptibility to hepatitis A. During their growth, most of the children acquire immunity through subclinical infection (sub-clinical infection means that one has hepatitis A infection with no clinical symptoms, no liver function damage but if that person is an antigen carrier, one can excrete virus and transmit hepatitis A). This kind of immunity is formed by production of antibodies after hepatitis A infection. It indicates previous hepatitis A virus attack, but if these are clinical symptoms and hepatomegaly, treatment should be instituted.
According to survey of China cities, children aging 2-10 years make up the chief human group suffering from hepatitis A; they consist mainly of children before and within school age. Statistics show that children aged 1-9 years have 52.6% positive hepatitis A antibodies, those aged 10-19 years have 98% and those over 29 years have 100% of positive hepatitis A antibodies. From this we can see the popularity of hepatitis a infection. It is commonly acknowledged that hepatitis A does not turn into chronic hepatitis. But there is report demonstrating that hepatitis A can similarly induce chronic hepatitis. (Weigl and Bach had reported that in 1283 cases of acute hepatitis A, 6.9% developed into chronic persisting hepatitis and 0.4% into chronic active hepatitis. In addition, Meier et al studied the serology, clinical biochemistry and a part of the liver biopsies of 25 hepatitis A patients and found that 20% manifested a persisting or chronic course with persistent increase of transaminase).
Oral transmission of disease
Hepatitis A virus is usually transmitted through the fecal-oral pathway. Stools from hepatitis A patients and subclinically infected sufferers are excreted with viruses; they contaminate food, water, tableware, utensils, toys and spread the disease. When the susceptible community increases to a certain proportion, a cyclic explosion of epidemic would occur. After an episode of epidemic spread, 80% of the susceptible community may be infected and then the epidemic stops. When the susceptible community increases to a certain proportion, the invasion of virus would evoke another episode of epidemic.
The present acknowledgement is that there is no persistent “antigen carrier” in hepatitis A virus and the origins of infection are the acute phase and subclinically infected patients. A life time immunity can only be achieved when human beings are continuously in a repeatedly infected situation. It is considered that hepatitis A virus can be alive for 12 months in fresh-water as well as salt water and for several days inside food. It will be dead if boiled in water for 5 minutes under 100°C. Therefore, the basic way to prevent hepatitis A is to put stress on individual hygiene, teach children to keep sanitary habits and prevent transmission of disease by mouth.
|
|
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a worldwide infectious disease. Its danger is more serious than other types of hepatitis. It is estimated that in the world 350 million people are “antigen carriers”, in which three fourths are Asians. The proportion of male to female is 6:1 in which at least 20% have various degrees of chronic active hepatitis and cirrhosis of liver and part of these cases may eventually turn into carcinoma of liver.
In China, about 40%-60% of the population has been infected by hepatitis B virus. In Hong Kong, about 40% of the population has been infected by this virus. The 1st peak period of infection by hepatitis B virus is before 10 years of age; the 2nd peak period is 30-40 years. Hepatitis B virus can pass through various body fluids (blood, semen, leukorrheal discharge, saliva, milk, menstrual blood, tears, urine and sweat) and be excreted, causing dissemination of infection, especially through blood and semen. Therefore, everyone carrying hepatitis B virus can transmit hepatitis B; those suffering from acute or chronic hepatitis B and the “antigen carriers” and other patients with positive antigen results (patients with cirrhosis or carcinoma of liver and other patients not having liver disease) are all origins of infection. In particular, the asymptomatic “antigen carriers” exist widely in the community, they remain unnoticed and therefore potentiate a greater degree of danger.
According to the epidemiological survey of our country in 1979-1980, these were over 120 million asymptomatic hepatitis B antigen carriers, the number of male is more than female. In Hong Kong, these are also nearly 600 thousand hepatitis B patients with positive surface antigen. As to age distribution in our country, the incidence is the highest before 10 years of age, and it decreases along with the increase of age. The highest incidence of hepatitis B is in the children group; the chief reason is that when the mother has hepatitis B, the infection is transmitted through the mother-child pathway.
Three possible ways of transmission
These are 3 possible ways of transmission in hepatitis B:
Mother-infant infection is the chief source of hepatitis B
Mother-infant infection is the most important pathway to transmission in hepatitis B. It is usually considered that in the community 35%-50% of carriers of hepatitis B surface antigens (antigen carrier) come from mother-infant transmission. In 1984, Beasiey pointed out that in countries over the world, the viruses in the maternal bodies with “positive” chronic hepatitis B surface antigen have different incidences of infection in the perinatal period. In Europe and America, the incidence rate is 10%, in Africa 25%-30%, Asia 30%-70% and in China 60%.
In recent years, Chinese investigations revealed that in screenings pregnant women with positive hepatitis B surface antigen had an incidence of 5%-10% in which 1/3 also have positive hepatitis B nuclear antigen (the commonly called double positive). If the mothers have “positive” hepatitis B surface antigen, 40%-50% of their children would become “antigen carriers”. If the mothers have also positive hepatitis B nuclear antigen, 63%-90% of their children would become hepatitis B “antigen carriers” within half a year. Not a few studies have demonstrated that if the mothers is “double positive”, among the siblings, there would appear a conspicuous “family coacervation phenomenon” of hepatitis B surface antigen (i.e. a number of people in a family infected by the virus and become “antigen carriers”).
In our country, the mother is the chief constituent of “family coacervation” of hepatitis B surface antigen, the mother’s effect on the infection of her children is strong and steady. Therefore, the prevention of transmission of virus from mother to children is of decisive significance to the control of hepatitis.
Caution on close contact infection
Besides mother-child transmission, close contact among family members (including baby-sitter) is also a very important way of transmission. Because there is an obvious phenomenon of hepatitis B surface antigen “family coacervation” among siblings, close contact can easily promote transmission of the infection. In addition, in different situations (in family, kindergarten, child-care center, school, hospital), the abrased mucosa or skin of the infant may be in contact with contaminated blood, drugs or medical instrument and then be infected by hepatitis B.
Increasing clinical evidences show that the main feature of hepatitis B virus infection is chronicity(慢性化). The danger to human beings is the formation of persistent infection; the smaller is the age of infection, the greater is the chance of becoming persistent infection. From the statistics, it is found that infants infected in the puerperium have a 80% possibility to become carrier of hepatitis B virus surface antigen, infection in childhood is about 30% and infection in adults, the possibility of becoming a persistent infection is below 5%. Therefore, infection by hepatitis B virus during infantile stage and childhood is most dangerous. It is estimated that in the community, 35%-50% of the people carrying hepatitis B virus surface antigen are infected during the maternal-infant puerperial period.
Attaching importance to treatment of pediatric hepatitis is the best policy
The prognosis of infantile pediatric hepatitis is not so good; most of the ones infected at newborn and infantile age would become chronic antigen carriers and chronic hepatitis sufferers. So, according to the above data, in the hepatitis B highly prevalent districts, the chance of infection by hepatitis B virus is very high and the prognosis is also very poor. Many infantile patients are infected not by their own will and they have to carry the disease throughout life with the repeated appearance of clinical symptoms of chronic hepatitis. Hepatitis virus affect their health in a life time and it is regretful that up to the present, many people do not care much for infantile and childhood chronic hepatitis; they do not understand the prevalence and harmfulness of the disease. Some people consider that there is no method to cure hepatitis radically and therefore they give up the treatment; others do not believe the effectiveness of Chinese drugs and refuse TCM therapy. Actually, these are extremely unwise considerations. From now onwards, the key point in prevention and treatment of hepatitis B should be put on infants and children in whom sufferers of hepatitis B can achieve clinical cure or not is of utmost importance.
|
|
Hepatitis C
The distribution of hepatitis C is worldwide showing that human beings are susceptible to hepatitis C virus. Among the sporadic hepatitis cases seen at the cities of many countries, hepatitis C takes up a proportion of 11.8%-23.8% in China and in 321 cases of acute sporadic virus hepatitis examinations, hepatitis C accounts for 6.2%. According to American statistics, hepatitis C accounts for 20%-40% of acute hepatitis cases and it is estimated that there are 200-300 thousand people suffering from hepatitis C every year.
Hepatitis C virus has not been successfully isolated and cultured at the present time and because the amount of virus nucleic acid and antigen in the patient’s blood is extremely minimal, it is not so easy to be detected by the commonly used methods. Recently, an investigation about hepatitis C in China revealed that the genetic constituent of hepatitis C virus is simple and only the type 2 and type 3 are in wide epidemic spread and its distribution also shown significant regional difference. In the south, the one in wide spread is type 2 and in the north, one half belongs to type 3. This investigation also certifies the ability of detecting Chinese hepatitis C positive transfusion donors by the international standard reagent and it was found that 13% of the virus “antigen carriers” could not be detected.
The chief source of infection in hepatitis C is virus carriers, including acute and chronic hepatitis C patients, subclinical patients and asymptomatic virus disseminators. They may persistently carry the virus over 12 years. It is now clear that the chief routes of hepatitis C infection are blood transfusion, blood products, injection, sexual life, mother-infant transmission and close contact. According to statistics, 50% of hepatitis C cases have no history of blood transfusion or use of blood products or history of injection; these cases are infected through close contact. Hepatitis C, in general, has comparatively mild symptoms, mostly anicteric and it is estimated that asymptomatic latent infections are even more. At least 40%-50% of hepatitis C patients would change into chronic hepatitis, the proportion is much higher than that in hepatitis B and in the end they have a higher tendency to develop into cirrhosis or carcinoma of liver. (Some data indicated asymptomatic hepatitis C patients can also develop into cirrhosis of liver and 60% of primary hepatic carcinoma patients show positive hepatitis C antibodies).
|
|
Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D virus is a kind of defective virus which requires the supplement of type B hepatitis virus to proceed replication and infection, so that it becomes pathogenic only with the company of hepatitis B virus infection. Due to the correlation of hepatitis D virus and hepatitis B virus, the infection can be divided intocommon infection and overlapping infection. The former is usually acute hepatitis, a few may develop severe hepatitis or turns into chronic hepatitis, but most of the acute hepatitis D cases would pass a benign course. The latter has already had liver damage due to the existing hepatitis B, therefore, most of the patients (70%-90%) would have aggravation of the disease and the tendency to turn into chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis of liver increases.
The distribution of hepatitis D is worldwide. According to statistics, at least 350 million people in the world are carriers of hepatitis B surface antigen, in which 5% are infected by hepatitis D virus; therefore, at least 15 million are concurrent sufferers of hepatitis D. In our country, it is chiefly found in Inner Mongolia, Tibet and Xinjiang. The mode of infection of hepatitis D is basically similar to hepatitis B, but mother-infant transmission is comparatively less. Its transmission is chiefly through the antigen carrying mother to the newborn child and close contact between family members through infected body fluids forming a horizontal transmission and “family coacervation” phenomenon may also occur (a number of persons infected in a family). But sexual transmission in hepatitis D is more important; the use of unclean injections or promiscuous sexual relationship (homosexuality or bisexuality) are the chief routes of infection. Hepatitis D cases often times develop into chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis of liver or may turn into severs hepatitis.
|
|
Hepatitis E
The epidemiology of hepatitis E is similar to hepatitis A, the spread being through fecal-oral transmission. Epidemic is induced by contamination of the source of water supply or by food ingestion. Its incidence, to a high degree, is related to the level of hygiene in the community, displaying in the form of local epidemics and fulminant epidemics. It has apparent seasonal characteristics and is frequently seen in the rainy seasons or after floods. In an investigation of 321 cases of sporadic acute virus hepatitis in our country, hepatitis E accounts for 10.28%. This disease has a higher incidence in the 20-40 years age group, male prevails over female. But in children, the infection usually belongs to the subclinical type and therefore may be neglected.
Hepatitis E may also be transmitted in daily life contact. In general, it is considered that this disease would not develop into chronic hepatitis, but its incidence is high and is more severe in pregnant woman, so it is easier to cause abortion and stillbirth. The mortality of this disease reaches 10%-20%, so one must treat it with prudence. Patients have a certain degree of immunity after hepatitis E infection and sufferers of second attack have not yet been discovered.
|
|
Hepatitis F & Hepatitis G
The above mentioned five types of hepatitis were ascertained in September 1989 at the International Meeting on non Type A non Type B Hepatitis and Blood Transmitting Infectious Diseases held in Japan. But according to later reports, there were also other types of hepatitis discovered, namely, hepatitis F and hepatitis G.
• Hepatitis F (HFV) and other intestinal tract transmitting new types of virus hepatitis had been reported in Britain, Italy, France, America, India and Germany and it was considered to be a double chain DNA virus.
• There were many reports about hepatitis G (HGV) and other blood transmitting new types of virus hepatitis. In our country, it was also found to be a RNA virus under the branch of yellow virus. It is transmitted through blood and can turn into chronic hepatitis. In addition, the GBV virus was also found, the type C of which produces infection through blood transmission and therefore, it is also called GBV-C/HGV. But, it is recognized now that there may be other hepatitis virus transmitted by blood.
|
| By WONG Kwok Hung
translated by Professor ZHENG Hua En in July 2005 |
(1) Talks on pediatric chronic virus hepatitis
General status of virus hepatitis
Virus hepatitis is a very common infections disease, existing widely in all races of human beings. Hong Kong, China and the countries in Southeast Asia are districts with high incidences of virus hepatitis. In the past, it was considered that only virus causing clinical manifestations of hepatitis can be defined as hepatitis virus, which, at the present time, is classified into 7 types. But now, it is identified that, besides hepatitis virus, parotitis virus, simple herpes virus, cytomegalovirus, EB virus, Coxsackie virus, ECHO virus, yellow fever disease virus, German measles virus all can cause pathological changes of chronic virus hepatitis in the infected children, although they have their respective clinical characteristics. These viruses are called in general “hepatophilic virus”, although they do not belong to the hepatitis group. When the child is infected by hepatophilic virus and develops chronic virus hepatitis, he would display the symptoms of TCM classified forms of chronic hepatitis as well as the sign of hepatomegaly. Cessation of advance of disease and the damage produced can be accomplished only by the administration of systemic TCM therapy. Therefore, if the diagnosis of chronic hepatitis is confined to the conventional standard, it is very likely that one may drop into the pitfall of misdiagnosis or may miss the diagnosis altogether.
The spread of virus is highly infectious as well as regional. In virus hepatitis, the B and C types draw most of the attention of human beings because, according to statistics, in the 300 million type B hepatitis virus carriers throughout the world, two thirds are located in Asia. Recent reports revealed that the majority of HBV infected patients in China had their infection initiated at infancy, especially through mother-child communication. Patients infected during infancy have a 90% possibility of developing chronic hepatitis in which 40% may aggravate to form cirrhosis of liver. In adult infected individuals, only 5% advance into chronic type B hepatitis, in which 5%-20% may develop cirrhosis of liver. So, the prevention and treatment of virus hepatitis should not be neglected, especially when the infection occurs during infancy because the harm done is more serious.
Hepatophilic virus diseases, like chronic type B hepatitis, are atypical or latent diseases. The patient’s early symptoms are usually mild, easy to be neglected and the diagnosis and treatment may be delayed. If found at the time when clinical symptoms are obvious, or at the stage of cirrhosis or carcinoma of liver, the optimal time for treatment is lost. Therefore, further understanding of the characteristics of pediatric chronic hepatitis and its early diagnosis and treatment are very important. In this way, malnutrition, underdevelopment and symptoms of different systems induced by chronic hepatitis may be prevented; and also this is one of the critical measures in the prevention of cirrhosis or carcinoma of liver in the subsequent adult years.
Initial virus hepatitis infection often occurs at infancy and childhood
In the present studies on virus hepatitis, type B hepatitis is commonly used as the chief object of investigation. Infancy and childhood are the prevailing years of type A and B hepatitis, especially type B hepatitis, in which spread through mother-child communication is extremely common. The dissemination of type C hepatitis is also achieved through mother-child communication as well as close contact. Type E hepatitis is comparatively less in children, and most of these cases belong to the sub-clinical type of infection and may be easily neglected by the patient and doctor. From the above data, it is shown that the majority of virus hepatitis infections occur during infancy or childhood. According to statistics in China, we can also find that damage from various types of viral infections hepatitis to infants and children is not only very common but also very serious.
In pediatric liver diseases, virus hepatitis B accounts for 75. 4%. According to data from Disease Prevention and Control Centre in mainland, 42% adult chronic hepatitis B patients were infected during childhood. The incidence of infection at birth is 40% in male and 20% in female. Advance of disease into cirrhosis and carcinoma of liver is closely related to HBV. Some reports revealed that in our country and Southeast Asia countries, infection by hepatitis B virus during infancy, childhood and adolescence, often times progressed into a chronic condition, persisting for years, over ten years or even for a life time. 70%-90% of these patients are prolonged “antigen carriers”, but they may show no significant symptoms. Their liver functions are normal, but 90% of liver biopsies reveal tissue damage. In the past, it was considered that pediatric hepatitis B pathological changes were mild and hepatitis remained in the guiescent condition which did not require treatment. This viewpoint may not be correct. In fact, the liver function (ALT) changes of pediatric hepatitis B patients often times are not consistent with tissue pathology due to disturbance of immune tolerance or immune function, so one should not wait for the occurrence of abnormal results of blood examination and ultrasound scan to start treatment. It is, therefore, advisable to make every effort to obtain early diagnosis and give early treatment according to the special features of pediatric liver disease.
Presently, large amounts of clinical study have revealed that chronic virus hepatitis is not caused by hepatitis virus alone and that virus has multiple characteristics, especially when it infects the host. It can produce a persistent virus infection which becomes the source of many common and frequently encountered diseases that may play an important role in causing failure of multiple systems of the body and in senility and death of human beings. In fact, human life is a life concurrent with virus as well as a life never ending in the struggle against virus. Not a few reports have demonstrated that virus infection may have attacked the fetus in the course of intrauterine development. For example:German measles virus infection may occur in early pregnancy, causing intrauterine infection which can induce abortion, mal-development and congenital anomaly. Cytomegalovirus infection also exists widely in the world, especially in developing countries, and in our country, the compliment – antibody test positive rate is 72.6%-76.84% in pregnant women, indicating that cytomegalovirus infection in adult females is rather high in which 1/4 may be primary infections. It endangers the fetus to develop into monsters, to be dead and aborted or acquire icterus neonatorum. Despite of successful pregnancy and delivery, some infants, within 3 months after birth, may develop purpura, hepatitis, encephalitis and pneumonia. Other viruses such as the human parvovirus, hepatitis virus, AIDS virus, simple herpes virus, cytomegalovirus and EB virus can permeate through the placenta and infect the fetus. Therefore, many primary virus infections occur at the important intrauterine, intra-vaginal, perinatal and infantile stages.
Popularity of virus infection in the world
From review of statistical data, we have an impression of the popularity of virus infection in the world; for example, in infantile stage, high susceptibility to respiratory syncytial virus (under one year old), adenovirus (7-24 months), human herpes virus type 6 (in America, England, Japan infants 6 months to 1 year anti HHV-6 nearly 100% positive). These reveal the direct cause of visceral pathological changes induced by virus infection in infants and it also reveals the unavoidable evidence of being infected by virus in human beings. So, an effective method for the improvement of human body constitution is to give more attention to the diagnosis and treatment of infantile diseases caused by virus, with the hope of decreasing the incidence of many frequently encountered diseases which are the result of liver function damage from viral infections.
Chronic virus hepatitis usually has its initial attack at the newborn stage or during infancy or childhood and its symptoms may be manifested later in the adult stage or when there is hepatic dysfunction as revealed by blood examination. But part of these cases might have already developed chronic hepatitis or even cirrhosis or carcinoma of liver. This may explain the tendency of seeing more and more younger cases of carcinoma of liver. It can be seen that hepatophilic viruses (including all types of hepatitis virus) affect greatly the health and development of children who have no ability to control the infection and even some are infected inside the uterus and doomed to carry the infection throughout life. It is regretful that many parents and clinical physicians do not pay enough attention on pediatric virus hepatitis; they may miss the diagnosis or make the wrong diagnosis, so that the optimal time of treatment slips away. How to discover early the children’s hepatitis is a question that all parents should concern eagerly.
The variability of clinical symptoms of pediatric liver disease: they have decisive effect on the child’s development and grown-up constitution.
Is pediatric virus hepatitis asymptomatic?
This concept is certainly wrong. In fact, when the human body is infected by virus, his immune system produces antibodies against the virus antigen; the antibodies neutralize and eliminate antigens. But during the course of immunologic response, the infected liver cells are also damaged, producing characteristic symptoms of hepatitis. The antigen-antibody complex substances deposit on other tissues of the body, causing simultaneous pathologic changes of extra-hepatic tissues and comparatively serious and persistent injury of other organs. The various clinical symptoms evoked are not characteristic and, so, are often neglected by physicians. Most clinical doctors do not pay attention to the fact that hepatophilic virus is actually the source of these diseases. For example, some auto-immune diseases are associated with arthritis, skin eruptions (pediatric eczema), glomerulonephritis, chronic thyroiditis and xeroderma. These are also some clinically mild symptoms such as nasal hypersensitivity, German measles, upper respiratory catarrh (common cold), gastroeuteritis (abdominal pain, diarrhea), peptic ulcer, biliary tract diseases, intestinal hypersensitivity, anemia, insomnia, long term headache, migraine, extreme tiredness, acne, oral ulcers, malnutrition and underdevelopment and menstrual disorders. If these patients are found in blood examination to have positive antigen and antibody, they may be considered as chronic asymptomatic hepatitis at the most.
In fact, these unnoticed symptoms may be the symptoms produced by frequent replication of hepatitis virus. It is considered by some that in virus hepatitis, the pathological changes inside the liver is pathogeneticallly not similar to those of the extra-hepatic. The intra-hepatic pathologic changes are caused by cellular immune response while the extra-hepatic is chiefly due to immunocomplex. So, clinically, the two pathological changes are not unanimous but contrarily they often show diversity. It is only when one is familiar with the clinical symptoms manifested in different stages of pediatric liver disease as classified by TCM forms, that it is possible to ascertain the diagnosis early and treat the patient early.
By WONG Kwok Hung
translated by Professor ZHENG Hua En in July 2005
Treatment of SARS with combined Chinese and western medicine – casual remarks and reflection
Introduction
The outbreak of infections atypical pneumonia in the recent month caused death of many people in the whole world, and aroused again attention of the medical profession on the virus. In fact, human beings should draw a lesson from this episode of SARS dissemination and make effort to prevent relapse of the spread of the virus, and at the same time, we should not ignore the combination of TCM and western medical treatment.
Atypical Pneumonia, from the viewpoint of virus disease – Atypical pneumonia is not fearful
Inadequate knowledge about the virus
The spread of atypical pneumonia has much frightened the people in Hong Kong. Not long before, some people in Hong Kong teased the panic buying of acetic acid and gauze masks in the interior, without sufficient self alert on the condition. The present status is that a widely growing sense of fear disseminates in Hong Kong, blaming the government incapable of preventing and treating the disease. In fact, these viruses cause infection upon people all over the world and many medical workers have been infected and some unfortunately died of it. We must admit that up to the present our knowledge about the virus is very inadequate.
Before the spring festival in Hong Kong, there were scattered epidemics of influenza in South china and some other parts of the world. The Hong Kong government had spent much money and efforts to prevent the attack of fowl influenza (including the death of park birds) upon human beings. At the present time, the weather, the geographic conditions, the communication developments and the rules of nature all can affect the dissemination of diseases. The larger epidemics of influenza, once in several years, have drawn much attention of the health and anti-epidemic departments. It is not strange to see that, in the recent years, antibodies inside the body of the people have gradually decreased on account of the effectiveness of preventive measures. And this, in turn, induces the present particularly large epidemic episode (it is said by some that the pathogenic agent is coronavirus or chlamydia) causing a world wide spread in which a small part of the infected people showed the complication of atypical pneumonia and some of them dies. According to traditional Chinese medicine it is dissemination of “spring pestilential disease”. The relation of the former fowl influenza causing large amounts of death with the present epidemic is still obscure.
Now, what kind of pathogenic virus causes the infection is not important because dissemination of the virus is, in fact, very wide. (Coronavirus usually causes human gastrointestinal symptoms, so, confirmation of the pathogen should still be done). Actually, the present so called atypical pneumonia presents “influenza” symptoms in the early stage and the Hong Kong epidemic is only part of the world “influenza” epidemic. The body build of infected individuals are different from one another and most people present only common cold symptoms which are not serious and therefore easily neglected.
TCM drugs yield effective results
Atypical pneumonia is not fearful, because it is only a complication of influenza in the late stage. TCM drugs were used to treat virus disease for thousands of years; TCM drugs and herbs, in fact, can effectively inhibit the progress of development of may virus disease and cut off the damage to the humane body by the virus. Early diagnosis and early prevention and treatment with TCM drugs allow influenza patients pass a smooth course and atypical pneumonia can be prevented and cured, and the mortality can be greatly lowered.
Serious cases come from secondary infection especially chronic liver disease
We are actually very fortunate because our ancestors had left us thousands of years of experience of prevention and treatment of diseases with TCM drugs, which are very effective in treating virus disease. Hong Kong and China have the tradition of using TCM drugs and most of the people there take TCM drugs in the early stage of the disease, so that, in this stage, it is comparatively easy to alleviate or eliminate the symptoms and also may lower the incidence of atypical pneumonia. Patients presenting atypical pneumonia symptoms usually belong to the serious or acute type and their health conditions are originally poor or they might have been suffering from chronic diseases (especially chronic liver disease) and having lowered resistance and detoxication capacity. These conditions promote the development of atypical pneumonia or if, in the recovery stage, there are secondary infection by bacteria or other pathogenic organisms, pneumonia, myocarditis, septicemia or other severe intervening episodes, serous conditions may be produced and death may result in some cases.
Virus Pneumonia are largely caused by hepatophilic viruses
In medical practice, it is demonstrated that virus pneumonia can be produced by a variety of viruses, including influenza a virus and parainfluenza virus, adenovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, cytomegalovirus, measles varicella, herpes virus, rhinovirus, coronavirus, Coxsackie virus, ECHO virus. Most of them are hepatophilic viruses that induce chronic hepatitis. It is not clear that the virus in the present epidemic disease is hepatophilic virus or not, but it is estimated that after the acute phase of the epidemic, the chronic hepatitis cases in various districts might turn into the “active stage”. Hepatogenic upper respiratory tract infection patients might increase significantly, presenting repeated nasal hypersensitivity, upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis and asthmatic clinical symptoms and signs. These cases would respond poorly to antibiotics, but if given TCM drugs for treatment of virus hepatitis, the therapeutic effect would be comparatively ideal.
The common characteristic for virus diseases
In fact, virus disease have a common characteristic, that is, in the early stage of infection, there are clinical symptoms of upper respiratory tract catarrh; these are nasal obstruction, mucous discharge, dryness of pharynx, sorethroat, hoarseness, headache, chilliness, fever, soreness of loin and back and pain of extremities. If sever, the patient may have a acute onset, dull appearance, lethargy, persistent high fever, chilliness, generalized pain and arthritic pain of extremities and may even have coughing, shortness of breath, nares flaring, asthmatic breathing, cyanosis of face and lips and eventually, coma, convulsions and death may ensue. Although the types of virus are may. The symptoms produced may be mild or sever. The clinical outcome different, but the TCM principle of treatment determination based on syndrome differentiation can suit every individual and obtain abrupt effectiveness. From the TCM point of view, no matter it is Sang Ju Yin (桑菊飲) or Yinqiao Jiedu Tang (銀翹降毒湯), Ma Xing Shi Gan Tong (麻杏石甘湯), they are all effective in treating acute and serious influenza. There are some effective elements in TCM drugs that can eliminate virus and terminate the progress of the disease. The marvelous point is that TCM drugs are definitely effective in dealing with virus diseases.
TCM drugs can drive virus out of the body
In the recent twenty years, in TCM therapy of chronic hepatitis caused by hepatophilic virus, we are extremely certain that some TCM formulas are effective in anti-virus treatment. In our clinic, among 3277 cases of abnormality of area of percussion dullness over hepatic region, those having liver stagnation lung dryness respiratory symptoms amounted to 1502 cases (occupying 45.83%). These patients had their liver returned to normal boundary after taking three or more parcels of TCM drugs. After 6 weeks of systemic TCM treatment, clinical cure was obtained. The use of these TCM drugs to combat virus together with western medicine treatment in the management of atypical pneumonia should yield a good result. The following is the formula which might be helpful for those engaged in the same pursuit.
| Tian Dong San Ren Yin Chun Tang (天冬三仁茵陳蒿湯) |
| Radiz Asparagi (天冬) | Semen Pruni (杏仁) | Herba Artemisiae Scopariae (綿茵陳) |
| Semen Trichosanthes (瓜蔞仁) | Fructus Arctil (牛子) | Radix Scutellariae (黃芩) |
| Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae (丹參) | Radix Bupleuri (柴胡) | Fructus Forsythiae (連翹) |
| Fructus Gardeniae (梔子) | Radix Astragali (黃蓍) | Pericarpium Citri Reticulate Viride (青皮) |
| Fructus Acuranti Immaturus (積實) | Radix Curcumae (郁金) | Radix Rehmanniae Praeparatae (熟地黃) |
| Radix Puerariae (葛根) | Semen Persicae (桃仁) |
Note:
l If high fever does not abate and the disease aggravates, the peripheral circulation collapses, and the asthmatic symptoms become severe, the addition of Gypsum Fibrosum (石膏), Herba Ephedrae (麻黃) should be considered.
2 If constipation occurs, Radix et Rhizoma Rhei (大黃) may be added; in case of bloody sputum or hemoptysis, Rhizoma Bletillae (白芨) may be added, and in severe cases, the boiled liquid medicine should be given by nasal feeding.
TCM and WM shall yield good results
The combined TCM and WM (western medicine) treatment is imperative, especially in cases requiring intensive care. When atypical pheumonia is complicated with toxic shock, there is failure of cardiopulmonary function and presence of virus myocarditis and this means further aggravation of the disease. WM treatment can give support systemically to the patient and relieve his symptoms (abatement of high fever, maintain patent respiratory passage, oxygen inhalation, relieve dehydration, and provide nutritional support). Proper use of corticosteroids can avoid abnormal immunologic response, so that atypical pneumonia patients may experience less suffering during the course of illness; and if combined with the above TCM drugs, the symptoms of the disease would be more relieved, the disease process more stable and the mortality further lowered.
The fight against influenza in Hong Kong and the interior during the fifties in the previous century is a recommendable experience. The old TCM formulas can be used today and corrected according to time, place and individual. It is worthwhile to mention that Ma Xing Shi Gan Tang (麻杏石甘湯) plus anti-virus TCM drugs give a definitely effective result in atypical pneumonia. Form the point of pharmacology, Gypsum Fibrosum (石膏) can clear heat and expel fie and also can decrease anxiety and stop thirsty sensation. Herba Ephedrae (麻黃) can promote sweating, calm asthmatic breathing, cause diuresis and eliminate edema. These drugs have good effect in the relief of high fever, thirst, lung heat and asthmatic cough, headache, generalized soreness, hypersensitivity and anti-shock in atypical pneumonia.
The above mentioned TCM mixtures often times can promote the excretion of antigen-antibody complex of the body in a short time. In western medicine, they used an extract from Herba Ephedrae (麻黃) called ephedrine hydrochloride to form cough mixtures which were used in the fifties to treat influenza and atypical pneumonia and were shown in the early stage to the effective in the abatement of fever. Cardiotonic, stoppage of asthma, improvement in failure of microcirculation and anti-shock are the characteristic pharmacologic effects of TCM drugs. They do not kill the viruses directly, but only drive them out, improve the internal environment of the human body and strengthen the immunologic capacity. It may be compared to a troop in war; it does not attack directly but aims at cutting off the enemies’ food supply. When the enemy troops have not enough food they would collapse themselves, without direct attack of the challenger. Although this strategy is different form the direct killing tactics of WM, it yields the same result.
| Prevention and treatment of SARS |
- Keep room humidity below 50℃: Spring pestilence occurs in spring at which time the weather has a high humidity and there is frequent alternation of coldness with hotness. The room humidity is high and this facilitates the spreading of virus loaded tiny droplets suspended in the air. Therefore, dwelling houses should choose natural ventilation and maintain the air fresh (like open the inlet hale of air conditioner, start the ventilator).
It is advisable to use home dwelling facilities to make an environment unlike spring, such as using the ventilator to form a humidity below 50 degrees (even lower, if no one stays in, but pay attention that it must not be too low, otherwise dryness of mouth and sorethroat may ensue). Use air conditioner to maintain a 17-20℃ room temperature. Because air in the room is in contact with the brass tube of air conditioner or ventilator, warm vaporized steam may condense to form water which would flow into the water container and be discarded. Dryness of room air would lessen greatly virus loaded droplets.
- Pay attention to personal hygiene: Patients having liver disease in the past should pay more attention to personal hygiene and rest. It is advisable to take more nutritious food (take more broth and soup that nourish yin (陰) and supplement kidney and also take protein hydrolysate and amino-acids. We should take less chicken, pigeon, mutton that might promote dryness and flaring up of fire. Stop drinking wine, no roasting food and acrid diets. If one feels dry and hot, one should take soups composed of Radix Puerariae as well as clearing, supplementing and cooling ingredients. The congee composed of duck eggs preserved in lime and salty meat is recommended. Drinks of the alkaline nature like cream soda are helpful because it can alkalinize the body fluid and increase resistance.
- Use ultra-violet rays for epidemic districts and boiling method for dwelling house in disinfection of virus: Some viruses do not have strong resistance to physical factors, for example, heat. Influenza virus loses its pathogenic capacity in several minutes under 56℃. In the common dwelling house, boiling is the usual method in disinfection of materials and the addition of soap powder in boiling for ten minutes eliminates bacteria and virus. Dryness, ultra-violet rays, alcohol, ether, carbolic acid and bleaching powder all can be used in the inactivation of viruses. Therefore, in epidemic districts, the use of ultra-violet rays and artificial exhaustion of moisture for air disinfection may be considered.
- Regular check for body temperature for infants and the old : Infants or children and the old in the family feeling discomfort should be routinely tested for body temperature every night to avoid neglect.
- Give back up support to medical professionals: Avoid contact with seriously ill patients. As to professional contact, the taking of TCM drugs for prevention and alleviation of symptoms is advisable. If there are common cold symptoms, one may consider the taking of the above TCM drugs.
- Prevent secondary bacterial infection: Influenza patients, often relief of clinical symptoms, relapse because of inadequate nutrition, rest and overwork. They show aggravation of cough, recurrence of high fever, purulent sputum and nasal discharge with yellowish, greenish color or blood tinged or even hemcptysis and chest pain. These presentations indicate that secondary bacterial infection had taken place. This condition is serious and medical treatment should be given early.
- On-the-spot Isolation : one of the preventive measures is to isolate the infected patients on-the-spot. It is necessary to post the message at the door of the infected house to alert passes-by, outsiders and relatives so as to avoid cross infection. From the medical point of view, it is not fearful to be infected as the body will produce antibody. More important is the close surveillance of the development of the disease and it is ideal to use TCM to combat the further development of the disease.
- Avoid infection, do not go to crowded places, if possible, do not go to hospital to visit patients; decrease visits to places with central air condition, because single air condition system may decrease chance of respiratory system infection.
- Earlier treatment is advisable: Patients with common cold symptoms like high fever, chilliness, generalized soreness of body, marked feeling of weakness, breathing with efforts and aggravation of illness should visit hospital early.
By WONG Kwok Hung,
on 10th April 2003
Translated by Professor Zheng Hua En on 18th April 2003
Hepatogenic “endocrine disorders”- disorders of sexual hormones
| Preface
The endocrine disorders seen in liver disease patients usually present singly (that is simple insufficiency of female sex hormones, simple insufficiency of thyroid hormones or diabetes), but sometimes, multiple disorders of hormones may exist. This article discusses only the affect of chronic liver disease on sex hormone disorder so that when endocrine disorder is encountered, one should consider the possibility of the presence of liver disease.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Endocrine disorder from viewpoint of TCM principle
According to the TCM classification of chronic hepatitis, the degree of severity of the disease is revealed through the symptoms of heart, liver and lung fire, symptoms of weakness of liver and kidney and results of physical examination. Therefore, basing on clinical manifestations, it is not difficult to find out the pattern of development of hepatophilic virus disease and endocrine disorder induced by chronic hepatitis can usually be diagnosed by the history and physical signs. If one can use the method of syndrome differentiation, adopt the therapeutic method of treating simultaneously the cause and symptoms, one may control the disease in the early stage, prevent impairment of liver function and avoid aggravation of the endocrine disorder.
When hepatophilic virus has invaded the body in the form of pestilential evil, and if the patient’s resistance is insufficient and the energy to drive out the evil is weak, the evil would hide in the blood and attack the five zang and six fu organs, disturb qi and blood causing impairment and gradual pathological changes of the latter. Clinical observation shows that deficiency of qi and blood is usually due to prolonged invasion of pestilential evil and persistent damage of five zang and six fu organs (especially infection during infancy and childhood). In fact, “endocrine disorder” is the most common consequence in the deficiency of qiand blood form of the TCM chronic hepatitis classification.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Endocrine disorder is extremely common
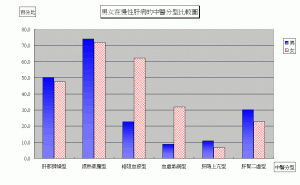
In various kinds of endocrine disorder of hepatogenic causes, the most common clinical types are “sex hormone disorder”, “diabetes” and “hepatogenic osteal malnutrition”. According to the statistics of our clinic, hepatogenic sex hormone disorder reaches 4.73% in which females occupy the majority, being 5.91% and males only 2.63%. As to hepatic osteal malnutrition, its amount is 13.69% in which males 12.53% (143:1141) and females 14.33% (291:2030).
According to the 3191 cases of abnormal margin of liver dullness in our clinic, it is obvious that significant difference exists between male and female patients in the TCM blockage of channels and stasis of blood form (male 22.86%, female 62.16%) and deficiency of blood and weakness of qi form (male 8.7%, female 31.96%). This difference indicates the necessity of early diagnosis and treatment of liver disease before the adolescent period in females. Females have to take up the burden of human generation; if they are infected by hepatophilic virus and cannot be treated in time, human beings would have the viral infection passed from generation to generation forming a vicious cycle.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comparison of male to female based on TCM form of chronic hepatitis
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Endocrine disorder in different stages
Endocrine disorder is extremely common in chronic hepatitis patients. Clinically, it is found that sex hormone disorders usually advance gradually; they may penetrate through all stages of life, from infancy, childhood, adolescence to climacteric and old age. The reason is that the majority of endocrine hormones metabolize in the liver (such as growth hormone, thyroid hormone, adrenocortical hormones, insulin, glucagons, male hormones, female hormones). When hepatitis occurs, endocrine disorders are produced in the body, manifesting clinical symptoms of different diseases. Therefore, strictly speaking, many common disease like hypoglycemia, abnormal thyroid function, diabetes, osteoporosis, sexual hormone disorders, maybe the result of chronic hepatitis. Treating disease from the fundamental requires understanding of the presence of chronic hepatitis. Systemic TCM therapy can often delay the progression of various endocrine disorders and combination of WH and TCM treatment can yield therapeutic effects with much less effort.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) Infancy and child stage
If chronic hepatitis patients were infected during infancy or childhood (from 2 months to 10 years), the abnormal liver function would cause endocrine disorder. The metabolic disturbances of hormones in liver disease are complicated and varied; they may lead to hypersomatotropinemia, decrease of growth hormone, disturbance of inactivation of renin and sub-aldosterone, abnormality of thyroid function, rise of insulin blood level and decrease of glucose tolerance.
In liver disease there may be inhibition of sex hormone stimulating hormone, leading to significant rise of basic level of blood estrogens and prolactin and decrease of male hormones. The above endocrine abnormality can dominate the child’s growth and development, especially type B and C hepatitis infection occurring directly through the mother-infant perpendicular infection. Such infection would show persistency and chronicity.
If the infant’s chronic hepatitis is not diagnosed or has been neglected by the doctor or parents, the chance of treatment is lost. Some of them stubbornly resist TCM therapy and let the course of disease prolonged, the disturbance of metabolism and endocrine hormones aggravated. In fact, TCM therapy cannot cure radically, but systemic therapy can often attain clinical cure. There may also be lowering of glucose tolerance or appearance of hypoglycemia. Pediatric patients in the hepatitis convalescent period have increased appetite and if not controlled properly, secondary obesity and fatty liver may result.
In addition, hormonal imbalance may cause disorder of nutritional metabolism and together with gastrointestinal absorptive disturbance; liver disease can lead to malnutrition. Due to calcium deficiency, the child may suffer from hepatogenic osteal malnutrition, delay of growth or even abnormal skeletal development. Therefore, hepatophilic infection may affect the child’s stature in two extremities: “ricketic dwarfism” and “secondary obesity”.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (2) Post adolescent stage
Female adolescence starts from 13 to 15 years of age. If the patient presents endocrine disorder at this time, she will have deficiency of estrogen and progesterone, and will lose the chance of developing secondary sexual characteristics and this effect may be carried throughout life. Because the anatomic structure and physiologic functions of female are different from male, so if she suffers from hepatophilic virus disease, the course would manifest a different feature.
In the early stage, liver stagnation and lung dryness form or wetness-heat vaporization form produces symptoms like wetness-heat of the stomache and intestines, wetness-heat of skin and wetness-heat of lower-jiao, the symptoms of these conditions are similar to the male. With the advance of disease, due to the difference in reproductive and endocrine systems, in the female post adolescent stage, hepatophilic virus disease cause liver stagnation, blockage of channels and stasis of blood which lead to abnormality of the blood clotting mechanism. The monthly menstruation becomes a potential damage to the chronic hepatitis patient. Menstrual disorder, menorrhagia, large amounts of blood clots, severe response before or after menstruation, severe dysmenorrheal, habitual abortion are common conditions that can induce gradually further disturbance of endocrine function, aggravate underdevelopment and malnutrition, anemia, hypoglycemia, hypoproteinemia, hypotension, hepatogenic infertility, hepatogenic osteal malnutrition or even formation of benign or malignant tumors of reproduction system, hepatic edema and secondary obesity.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common characteristics of female patients with sex hormone disorder
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (3) Periclimacteric stage
If the disease progresses into the climacteric stage (45-50 years), the degree of disorder of endocrine system depends on the severity of hepatophilic virus disease. The usual picture is increasing severity of clinical symptoms; early appearance of weakness of liver and kidney causes the patient’s apparent senility and prolonged suffering from symptoms of weakness of liver and kidney. When a woman enters climacteric stage, her ovarian function gradually weakens, the ovarian follicles can not develop in the regular pattern and there is no corpus luteum formation. The endometrium remains in the proliferative phase, the regular cyclic changes disappear, the menstrual interval is prolonged and the progressive decrease of menstrual blood indicates impending amenorrhea.
Because of decrease of female sex hormones, under the condition of appearance of flaring up of liver fire symptoms following liver stagnation and lung dryness and deficiency of yin in liver and kidney, the female patient may suffer from climacteric symptoms such as flush of face and ear, feverish and hot sensation of five visceral organs, migraine, headache, vertigo, tinnitus, imbalance of auricular fluid, palpitation, insomnia, tremor of hands, hidrosis, boldness, pigmentation or generalized senile plagues, apparent restlessness and depression.
If estrogen insufficiency causes deprivation of calcium, hepatic asteal malnutrition may result. Prolonged existence of liver, heart and lung fire causes consumption of kidney fluide, leading to decreased ability of kidney fluid to nourish bones and tendons. Therefore, the patient is prone to develop osteoporosis and hyperosteogeny (spur). Hepatic osteal malnutrition patients often suffer from wondering joint pain, swelling and deformity of urticulations, pain of bones and tendons and in severe cases, progressive rheumatoid arthritis, acute gout, shortening of body height, humpback or fracture. When the patient passes into menopause and old age, her genital organs gradually become atrophic, her metabolism slows down and she possesses a fat stature and becomes susceptible to senile vaginitis.
Statistics by scholars in Hong Kong have show that 60% of climacteric women suffer from insomnia and bone disease. They suggest that these women should be treated with medication for estrogen deficiency to alleviate symptoms like flush, insomnia and bone disease, and also for climacteric heart disease, osteoporosis and senile dementia. For female patients with chronic hepatitis, it is advisable to have treatment width systemic TCM therapy followed by sex hormone medication directed by physicians to cape with the clinical symptoms induced by “sex hormone disorder”. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Introduction of cases
In fact, the ill effect of hepatophilic virus on female is more serious than on male. It is because the investigation and treatment of the clinical symptoms of many females have not been raised to the level of hepatogenic disease, that the prolonged illness of many females are not much improved. The following clinical cases are introduced for the elucidation of the effectiveness of TCM drugs in treatment of endocrine disorders.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Case 1
Chan – (code number 1973), female, age 33 years. Her first visit was in October 1999 complaining chiefly of chilliness, fatigue, constipation, bowl movements once in 2-4 days. For a long time, she suffered from repeated acne and generalized sweat stains and in the recent years, she had abundant leukorrheal discharge of greenish yellow color associated with purities of vulva. The diagnosis by western medical doctors was moniliasis, but repeated treatment did not cure the disease. She had blood examination last year and found hypofunction of thyroid which was not treated.
Physical examination: body height 1.7m. weight 56 kg, BMI = 19.37, long limbs, lean, female secondary sexual characteristics not apparent, pulse slow, 52/minute, percussion tenderness over hepatic region, hepatomegaly of 3 cm, (+) pitting edema of lower extremities. The diagnosis was chronic hepatitis, with TCM classification of wetness-heat vaporization form (wetness-heat of stomache, intestines and lower-jiao) and endocrine disorder (hypothyroidism and estrogen deficiency).
After taking 3 parcels of TCM drugs, she had belching, distension of abdomen, abdominal pain, bowl movements once a day. Her digestion was poor, sleeping not so good, urine yellowish but her liver was normal. Then, TCM drugs were not taken for nearly 25 days because of work. At the return visit, her menstruation had just occurred for one day, but its amount was large; she also had constipation, oral ulcers, swelling pain of gingivae and a poor mental state. She had common cold symptoms for 2 days and also had numbness of limbs, shortness of breath, enlargement of tongue with furrows and the first relapse of hepatomegaly of 3 cm. After taking 3 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver returned to normal. Systemic TCM therapy continued for 5 weeks. She was followed up afterwards.
After TCM therapy, she received one contraceptive injection. Thereafter, she had significant improvement in secondary sexual characteristics, especially the breasts. Three months later, her menstrual blood amount decreased greatly, the menstrual days shortened and purulent leukorrheal discharge disappeared. Her gynecological illness had been cured.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Case 2
Yang-, (code number 2815), female, age 34 years. She first visited the clinic in March 2002 with the complaint of insomnia and a diagnosis of depression. She was taking for a long time sleeping pills and psychotic drugs. She also suffered from acne, epigastria discomfort after wine drinking, occasional hematochezia; her menstruation delayed, amount decreased and with clots and dysmenorrheal.
Physical examination: height 1.68m. weight 51 kg, BMI = 18.08, slender stature, long limbs, hairy lower extremities, skin dry, coarse and pale yellowish with scattered patchy depigmentation areas (vitiligo), lips lineate and with desquamation, tongue clean, hypochondriac anomaly, hepatomegaly of 1.5 cm, percussion dullness over splenic region. The diagnosis was hepatomegaly for investigation, sexual hormone disorder, hepatogenic psychoneurotic disease (depression), vitiligo.
After taking 3 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver was normal and the splenic dullness turned typanitic. She still experienced fatigue, had bowl movements four times a day and also flatulence, insomnia, poor sleeping and generalized soreness of body. Pulse 100/minute. TCM drugs later could help her sleeping better but she was dreamful, tired and occasionally anxious. She had loin pain, flatulence and her bowl movements became smooth, being once a day. Totally, 59 parcels of TCM drugs were taken, after which clinical cure was obtained and she was followed up.
A return visit was made six months later, at which time she was free of psychotic symptoms and her sleeping was good, being over 5 to 6 hours a night. She still had occasional loin pain, hidrosis and pruritus ani; pulse 88/minute, tongue showing teeth prints, (+) edema of lower extremities, liver margin normal.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
By WONG Kwok Hung Published on 6th March 2003 Translated by Professor Zheng in May 2005 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||