|
In the past, it was considered that only those which could induce clinical manifestations of hepatitis were ascertained as hepatitis virus. The latter is known, at the present time, to include seven types. In fact, besides hepatitis virus, many other viruses can also produce hepatitis and possess “hepatophilic” characteristics; these are the parotitis virus, simple herpes virus, cytomegalovirus, EB virus, Coxsackie virus, ECHO virus, yellow fever virus, German measles virus. These viruses have their respective clinical features, so they do not belong to the hepatitis virus group, but should be called in general “hepatophilic virus”.
Although these viruses are not called hepatitis virus but it does not mean that they do not induce hepatic infection (acute or chronic) of the host, leading to hepatomegaly and, at the same time, to hepatitis symptoms and extrahepatic manifestation and complications. Therefore, if clinical diagnosis is made on the basis of the past standard, large amounts of early and mild cases as well as cases with extrahepatic symptoms as chief manifestation would lose the chance of early treatment. In other words, “hepatophilic virus” should include several types of hepatitis virus and all related viruses that can cause symptoms of hepatitis. “Hepatophilic virus disease” should refer to patients with abnormal margin of liver dullness and with prolonged, repeated disease course indicating damage of multiple systems. These manifestations are the various clinical diseases caused by liver function damage.
Chronic hepatophilic virus disease is clinically a very common and typical virus disease. These viruses can evoke hepatitis after entering the human body. In spite of occultation of the virus and chronicity of the infection causing the induced clinical symptoms atypical and, therefore, often being neglected, yet the immune response of the body increases day by day. The latter condition promotes revelation of clinical symptoms and eventually leads to “hepatomegaly” which is a long lasting sign. This sign is the best object for the clinician to judge the effectiveness of therapy.
|
| By WONG Kwok Hung
translated by Professor ZHENG Hua En in July 2005 |
Category Archives: For woman
Hepatogenic “endocrine disorders”- disorders of sexual hormones
| Preface
The endocrine disorders seen in liver disease patients usually present singly (that is simple insufficiency of female sex hormones, simple insufficiency of thyroid hormones or diabetes), but sometimes, multiple disorders of hormones may exist. This article discusses only the affect of chronic liver disease on sex hormone disorder so that when endocrine disorder is encountered, one should consider the possibility of the presence of liver disease.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Endocrine disorder from viewpoint of TCM principle
According to the TCM classification of chronic hepatitis, the degree of severity of the disease is revealed through the symptoms of heart, liver and lung fire, symptoms of weakness of liver and kidney and results of physical examination. Therefore, basing on clinical manifestations, it is not difficult to find out the pattern of development of hepatophilic virus disease and endocrine disorder induced by chronic hepatitis can usually be diagnosed by the history and physical signs. If one can use the method of syndrome differentiation, adopt the therapeutic method of treating simultaneously the cause and symptoms, one may control the disease in the early stage, prevent impairment of liver function and avoid aggravation of the endocrine disorder.
When hepatophilic virus has invaded the body in the form of pestilential evil, and if the patient’s resistance is insufficient and the energy to drive out the evil is weak, the evil would hide in the blood and attack the five zang and six fu organs, disturb qi and blood causing impairment and gradual pathological changes of the latter. Clinical observation shows that deficiency of qi and blood is usually due to prolonged invasion of pestilential evil and persistent damage of five zang and six fu organs (especially infection during infancy and childhood). In fact, “endocrine disorder” is the most common consequence in the deficiency of qiand blood form of the TCM chronic hepatitis classification.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Endocrine disorder is extremely common
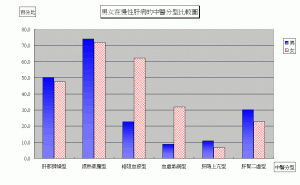
In various kinds of endocrine disorder of hepatogenic causes, the most common clinical types are “sex hormone disorder”, “diabetes” and “hepatogenic osteal malnutrition”. According to the statistics of our clinic, hepatogenic sex hormone disorder reaches 4.73% in which females occupy the majority, being 5.91% and males only 2.63%. As to hepatic osteal malnutrition, its amount is 13.69% in which males 12.53% (143:1141) and females 14.33% (291:2030).
According to the 3191 cases of abnormal margin of liver dullness in our clinic, it is obvious that significant difference exists between male and female patients in the TCM blockage of channels and stasis of blood form (male 22.86%, female 62.16%) and deficiency of blood and weakness of qi form (male 8.7%, female 31.96%). This difference indicates the necessity of early diagnosis and treatment of liver disease before the adolescent period in females. Females have to take up the burden of human generation; if they are infected by hepatophilic virus and cannot be treated in time, human beings would have the viral infection passed from generation to generation forming a vicious cycle.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comparison of male to female based on TCM form of chronic hepatitis
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Endocrine disorder in different stages
Endocrine disorder is extremely common in chronic hepatitis patients. Clinically, it is found that sex hormone disorders usually advance gradually; they may penetrate through all stages of life, from infancy, childhood, adolescence to climacteric and old age. The reason is that the majority of endocrine hormones metabolize in the liver (such as growth hormone, thyroid hormone, adrenocortical hormones, insulin, glucagons, male hormones, female hormones). When hepatitis occurs, endocrine disorders are produced in the body, manifesting clinical symptoms of different diseases. Therefore, strictly speaking, many common disease like hypoglycemia, abnormal thyroid function, diabetes, osteoporosis, sexual hormone disorders, maybe the result of chronic hepatitis. Treating disease from the fundamental requires understanding of the presence of chronic hepatitis. Systemic TCM therapy can often delay the progression of various endocrine disorders and combination of WH and TCM treatment can yield therapeutic effects with much less effort.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) Infancy and child stage
If chronic hepatitis patients were infected during infancy or childhood (from 2 months to 10 years), the abnormal liver function would cause endocrine disorder. The metabolic disturbances of hormones in liver disease are complicated and varied; they may lead to hypersomatotropinemia, decrease of growth hormone, disturbance of inactivation of renin and sub-aldosterone, abnormality of thyroid function, rise of insulin blood level and decrease of glucose tolerance.
In liver disease there may be inhibition of sex hormone stimulating hormone, leading to significant rise of basic level of blood estrogens and prolactin and decrease of male hormones. The above endocrine abnormality can dominate the child’s growth and development, especially type B and C hepatitis infection occurring directly through the mother-infant perpendicular infection. Such infection would show persistency and chronicity.
If the infant’s chronic hepatitis is not diagnosed or has been neglected by the doctor or parents, the chance of treatment is lost. Some of them stubbornly resist TCM therapy and let the course of disease prolonged, the disturbance of metabolism and endocrine hormones aggravated. In fact, TCM therapy cannot cure radically, but systemic therapy can often attain clinical cure. There may also be lowering of glucose tolerance or appearance of hypoglycemia. Pediatric patients in the hepatitis convalescent period have increased appetite and if not controlled properly, secondary obesity and fatty liver may result.
In addition, hormonal imbalance may cause disorder of nutritional metabolism and together with gastrointestinal absorptive disturbance; liver disease can lead to malnutrition. Due to calcium deficiency, the child may suffer from hepatogenic osteal malnutrition, delay of growth or even abnormal skeletal development. Therefore, hepatophilic infection may affect the child’s stature in two extremities: “ricketic dwarfism” and “secondary obesity”.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (2) Post adolescent stage
Female adolescence starts from 13 to 15 years of age. If the patient presents endocrine disorder at this time, she will have deficiency of estrogen and progesterone, and will lose the chance of developing secondary sexual characteristics and this effect may be carried throughout life. Because the anatomic structure and physiologic functions of female are different from male, so if she suffers from hepatophilic virus disease, the course would manifest a different feature.
In the early stage, liver stagnation and lung dryness form or wetness-heat vaporization form produces symptoms like wetness-heat of the stomache and intestines, wetness-heat of skin and wetness-heat of lower-jiao, the symptoms of these conditions are similar to the male. With the advance of disease, due to the difference in reproductive and endocrine systems, in the female post adolescent stage, hepatophilic virus disease cause liver stagnation, blockage of channels and stasis of blood which lead to abnormality of the blood clotting mechanism. The monthly menstruation becomes a potential damage to the chronic hepatitis patient. Menstrual disorder, menorrhagia, large amounts of blood clots, severe response before or after menstruation, severe dysmenorrheal, habitual abortion are common conditions that can induce gradually further disturbance of endocrine function, aggravate underdevelopment and malnutrition, anemia, hypoglycemia, hypoproteinemia, hypotension, hepatogenic infertility, hepatogenic osteal malnutrition or even formation of benign or malignant tumors of reproduction system, hepatic edema and secondary obesity.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common characteristics of female patients with sex hormone disorder
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (3) Periclimacteric stage
If the disease progresses into the climacteric stage (45-50 years), the degree of disorder of endocrine system depends on the severity of hepatophilic virus disease. The usual picture is increasing severity of clinical symptoms; early appearance of weakness of liver and kidney causes the patient’s apparent senility and prolonged suffering from symptoms of weakness of liver and kidney. When a woman enters climacteric stage, her ovarian function gradually weakens, the ovarian follicles can not develop in the regular pattern and there is no corpus luteum formation. The endometrium remains in the proliferative phase, the regular cyclic changes disappear, the menstrual interval is prolonged and the progressive decrease of menstrual blood indicates impending amenorrhea.
Because of decrease of female sex hormones, under the condition of appearance of flaring up of liver fire symptoms following liver stagnation and lung dryness and deficiency of yin in liver and kidney, the female patient may suffer from climacteric symptoms such as flush of face and ear, feverish and hot sensation of five visceral organs, migraine, headache, vertigo, tinnitus, imbalance of auricular fluid, palpitation, insomnia, tremor of hands, hidrosis, boldness, pigmentation or generalized senile plagues, apparent restlessness and depression.
If estrogen insufficiency causes deprivation of calcium, hepatic asteal malnutrition may result. Prolonged existence of liver, heart and lung fire causes consumption of kidney fluide, leading to decreased ability of kidney fluid to nourish bones and tendons. Therefore, the patient is prone to develop osteoporosis and hyperosteogeny (spur). Hepatic osteal malnutrition patients often suffer from wondering joint pain, swelling and deformity of urticulations, pain of bones and tendons and in severe cases, progressive rheumatoid arthritis, acute gout, shortening of body height, humpback or fracture. When the patient passes into menopause and old age, her genital organs gradually become atrophic, her metabolism slows down and she possesses a fat stature and becomes susceptible to senile vaginitis.
Statistics by scholars in Hong Kong have show that 60% of climacteric women suffer from insomnia and bone disease. They suggest that these women should be treated with medication for estrogen deficiency to alleviate symptoms like flush, insomnia and bone disease, and also for climacteric heart disease, osteoporosis and senile dementia. For female patients with chronic hepatitis, it is advisable to have treatment width systemic TCM therapy followed by sex hormone medication directed by physicians to cape with the clinical symptoms induced by “sex hormone disorder”. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Introduction of cases
In fact, the ill effect of hepatophilic virus on female is more serious than on male. It is because the investigation and treatment of the clinical symptoms of many females have not been raised to the level of hepatogenic disease, that the prolonged illness of many females are not much improved. The following clinical cases are introduced for the elucidation of the effectiveness of TCM drugs in treatment of endocrine disorders.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Case 1
Chan – (code number 1973), female, age 33 years. Her first visit was in October 1999 complaining chiefly of chilliness, fatigue, constipation, bowl movements once in 2-4 days. For a long time, she suffered from repeated acne and generalized sweat stains and in the recent years, she had abundant leukorrheal discharge of greenish yellow color associated with purities of vulva. The diagnosis by western medical doctors was moniliasis, but repeated treatment did not cure the disease. She had blood examination last year and found hypofunction of thyroid which was not treated.
Physical examination: body height 1.7m. weight 56 kg, BMI = 19.37, long limbs, lean, female secondary sexual characteristics not apparent, pulse slow, 52/minute, percussion tenderness over hepatic region, hepatomegaly of 3 cm, (+) pitting edema of lower extremities. The diagnosis was chronic hepatitis, with TCM classification of wetness-heat vaporization form (wetness-heat of stomache, intestines and lower-jiao) and endocrine disorder (hypothyroidism and estrogen deficiency).
After taking 3 parcels of TCM drugs, she had belching, distension of abdomen, abdominal pain, bowl movements once a day. Her digestion was poor, sleeping not so good, urine yellowish but her liver was normal. Then, TCM drugs were not taken for nearly 25 days because of work. At the return visit, her menstruation had just occurred for one day, but its amount was large; she also had constipation, oral ulcers, swelling pain of gingivae and a poor mental state. She had common cold symptoms for 2 days and also had numbness of limbs, shortness of breath, enlargement of tongue with furrows and the first relapse of hepatomegaly of 3 cm. After taking 3 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver returned to normal. Systemic TCM therapy continued for 5 weeks. She was followed up afterwards.
After TCM therapy, she received one contraceptive injection. Thereafter, she had significant improvement in secondary sexual characteristics, especially the breasts. Three months later, her menstrual blood amount decreased greatly, the menstrual days shortened and purulent leukorrheal discharge disappeared. Her gynecological illness had been cured.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Case 2
Yang-, (code number 2815), female, age 34 years. She first visited the clinic in March 2002 with the complaint of insomnia and a diagnosis of depression. She was taking for a long time sleeping pills and psychotic drugs. She also suffered from acne, epigastria discomfort after wine drinking, occasional hematochezia; her menstruation delayed, amount decreased and with clots and dysmenorrheal.
Physical examination: height 1.68m. weight 51 kg, BMI = 18.08, slender stature, long limbs, hairy lower extremities, skin dry, coarse and pale yellowish with scattered patchy depigmentation areas (vitiligo), lips lineate and with desquamation, tongue clean, hypochondriac anomaly, hepatomegaly of 1.5 cm, percussion dullness over splenic region. The diagnosis was hepatomegaly for investigation, sexual hormone disorder, hepatogenic psychoneurotic disease (depression), vitiligo.
After taking 3 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver was normal and the splenic dullness turned typanitic. She still experienced fatigue, had bowl movements four times a day and also flatulence, insomnia, poor sleeping and generalized soreness of body. Pulse 100/minute. TCM drugs later could help her sleeping better but she was dreamful, tired and occasionally anxious. She had loin pain, flatulence and her bowl movements became smooth, being once a day. Totally, 59 parcels of TCM drugs were taken, after which clinical cure was obtained and she was followed up.
A return visit was made six months later, at which time she was free of psychotic symptoms and her sleeping was good, being over 5 to 6 hours a night. She still had occasional loin pain, hidrosis and pruritus ani; pulse 88/minute, tongue showing teeth prints, (+) edema of lower extremities, liver margin normal.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
By WONG Kwok Hung Published on 6th March 2003 Translated by Professor Zheng in May 2005 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The relation of liver disease with “epression” and “postpartum depression”
| Preface
According to data from Health Bureau of Hong Kong, patients suffering from depression have increased in the past three years, from 9,700 more persons in 1999-2000 to over 13,700 in the previous years and the majorities are females, between 40-60 years of age, accounting for 30% of new cases in each year. The statistics of the Hospital Authority showed that patients with depression during the year 2001-2002 had increased 41%. This is an indication of the degree of popularity of the disease. Recently, there were several episodes occurring one after another, of committing suicide through jumping from a building and it was reported that these individuals were all sufferers of postpartum depression. This article attempts to elucidate the cause of depression and postpartum depression from the viewpoint of TCM and to reveal the disease manifestation of postpartum depression on the basis of chronic hepatic disease.
|
|
| Depression
According to TCM, depression is an extremely common clinical neural and psychotic condition induced by stagnation of liver qi . It was mentioned that liver disease can produce many neurasthenia symptoms, and chronic hepatitis can cause clinical damage of many systems, so that these patients may suffer from symptoms of various systems in different stages of disease. Modern medicine promotes the development of anatomico-pathalogy and cytopathology and pays attention especially to research and diagnosis of pathologic changes of visceral organs, trying in all ways to find out the “focus” and substantiating continuously the methods of diagnosis. Diagnostics has shown radical changes and diagnostic means and accessory instruments have increased greatly, but there is a tendency of things to fall into another extremity and it seems now that physical examination of patients has changed to merely checking up of laboratory examination results. Therefore, the traditional “diagnosis by syndrome differentiation” and ‘treating the fundamental” therapeutic measures are often neglected and severe neural and psychotic symptoms may be simply diagnosed as psychosis and treated as such without a time limit.
Anti-depression treatment can control illusion and emotional instability, but prolonged intake of psychotic drugs may induce side effects like stiffness of muscles, tremor, inability to sit quietly and slowness of motion. It can also induce sleepiness, edema, salivation, vertigo, difficulty in urination and defecation, palpitation and muscle spasm. Whether long term anti-depression treatment an ideal therapy or not is a matter of individual consideration. But if these patients are on the base of chronic liver disease, systemic TCM therapy is still a method of choice.
|
|
|
Chronic liver disease patients susceptible to postpartum depression
Obstetricians and gynecologists point out that emotional fluctuation after delivery is due to the affect of hormonal changes in women who have to endure also the stress of looking after their babies, so that three months postpartum is the “high risk period” of postpartum depression. In the early stage, the symptoms may appear as early as 3 – 5 days after delivery, including moodiness, liable to crying, insomnia and restlessness. If the condition has changed to postpartum depression, the patient experiences fatigue, insomnia, loss of appetite, anxiety and frightfulness; in severe cases, there may be auditory hallucination, idea of committing suicide and of killing the baby.
Delivery is in fact the time of induction of the relapse of hepatophilic virus disease, because during pregnancy the liver has a greater burden, so that nutrition may be insufficient and endocrine changes often become the inducing factor of hepatic psychoneurotic disease. Therefore, women with chronic hepatitis are prone to have psychoneurotic symptoms of postpartum depression after delivery. Among all kinds of depressive states, postpartum depression is the one with the closest relation to hepatophilic virus infection. Clinically, it is common to see female chronic hepatitis patients, who have obtained clinical cure after systemic TCM therapy, experience relapse of hepatomgaly following pregnancy and delivery and require a repeated systemic treatment of TCM drugs.
|
|
|
Traditional Chinese Medicine possesses exquisite knowledge on postpartum depression
From the TCM viewpoint on etiology, it is not difficult to find that TCM has accumulated meticulous observation and therapeutic experience in female postpartum neural and psychotic symptoms. For example:
l Postpartum jaundice: postpartum deficiency of blood and stagnation of qi, jaundice of skin of body, eyes face, fatigue of limbs. l Postpartum hypochondriac pain: postpartum damage of liver, deficiency of blood and stagnation of qi; the liver governs tendons which spread over the hypochondria so that there is distensive pain over the chest and hypochondriac intercostal spaces. l Postpartum panic: due to postpartum weariness, fright and tiredness, excessive loss of blood, weakness of heart qi with mental instability, causing the heart to be kept in a state of agitation and frightening, the patient showing mental disturbance, fixation of the eyes or talking nonsense. l Postpartum insomnia: postpartum excessive loss of blood, deprivation of nourishment to the mind, the patient therefore not able to sleep well, appearing anxious, perspiring or having flush of face and feeling thirsty. l Postpartum absent-minded: after delivery, heart blood being insufficient, disorder of nutrition leading to mental instability, staring eyes without expression and postpartum edema. l Postpartum restlessness of deficiency type: postpartum injury of qi and blood, flaring up of asthenic fire or rushing up of qi and blood, restlessness of heart, unsmooth flow of qi, anger blasting out without reason, frequent occurrence of restlessness, vomiting, vexation, asphyxiating pain in the chest. l Postpartum mania: deficiency of blood after delivery, the heart devoid of nutrition, fever associated with unsmooth lochial discharge, talking wildly, inability to recognize people, face greenish and lips pale, limbs cold or keeping quiet without a word or widely opened eyes staring straight forward.
At the critical periods of “pregnancy”, delivery” and “postpartum”, woman with chronic hepatitis may suffer from damage of liver function due to “deficiency of blood” or overload strain of the body. They are prone to develop “depression” and its related symptoms and postpartum depression is the most common type of the disease. It may finally cause death of mother and baby. Therefore, attention should be paid keenly by family members of the patient and systemic TCM therapy should be instituted in time for prevention of further development of the disease. Chronic hepatitis female patients in the postpartum period should be routinely examined for percussion dullness of the hepatic region and “liver disease” should be treated if necessary.
With the pass of time, liver disease patients who have not given systemic TCM therapy inevitably go into the climacteric stage, at which time sexual hormones decrease, disturbance of autonomic system intervenes. Consequently, there is the occurrence of climacteric syndrome and perhaps the following “senile dementia” (老年性痴呆). In fact, the patient’s psychoneurotic symptoms are the result of brain and neural tissue damage following hepatophilic virus infection and clinically they show psychoneurotic symptoms of various degrees. |
|
|
Virus infection concerns health in a life time When hepatophilic virus infection occurs in the intrauterine fetus or during infancy, it affects the victim throughout life. In one’s life time, from birth, growing up and mature, old age and death, no period is not related to the effect of hepatophilic virus infection in the body. The day will come when people recognize that the methods of treating “diseases” are in fact chiefly the clinical therapeutic measures of “prevention and systemic treatment of hepatophilic virus infection, prevention of liver function damage and treating in time of various complications of liver disease. The pathological changes of the nervous system caused by hepatophilic virus inflection can be divided into acute and chronic. In chronic liver disease patients, the concentration of “antigen-antibody complex” varies with the pass of time and its affect on brain and nervous tissue results in edema, degeneration, thinning of cerebral cortex, disappearance of neurons and nerve fibers or even patchy necrosis of deep layer of cortex. Due to damage of auto-immune function, the patient’s detoxification power of liver becomes abnormal, vitamin B complex is deficient and together with the defect of enzyme leading to the blockage of the metabolism, so that some toxic substances can pass into systemic circulation and interfere with cerebral function and nerve impulse activity. This is the fundamental cause of human psychoneurotic disease. In the life time of an individual, besides external factors (e.g. alcohol addiction, drug taking, infection, medical drugs) interfering with liver function, in certain periods of life, there may exist some factors which can induce “hepatic encephalopathy” (肝性腦病) : the most conspicuous is the adolescent period, pregnancy, postpartum, climacteric and old age. In these conditions, the effect of hepatophilic virus forms the base of liver function disturbance. Different inducing factors (e.g. loss of blood, endocrine disorder etc.) affect the body immunologic power in different manners, but invariably the end result is damage of the brain nervous tissues with significant clinical symptoms of hepatic cerebral-neural disease. If children with chronic liver disease go into the adolescent period, their development would be frustrated by endocrine disorder, malnutrition and metabolic disturbance following impairment of liver function. The growth of the child is slow or there is anomaly of skeletal development (hepatogenic malnutrition and underdevelopment or hepatic osteal malnutrition) or secondary obesity. A small number of the male sick children have a feminine type of breast development. Their external genitalia and testicles are atrophic, their body hair scarce. Some girls may develop a lean and high stature due to disorder of sexual hormones; their limbs are long, hairy and their secondary sexual characteristics underdeveloped. These teen age adolescents are prone to develop “disorder of thought”. Disorder of thought Recently some scholars pointed out that disorder of thought is due to cerebral changes from virus infection and the inducing factor is stress and environmental changes. This disease is an early type of abnormal psychotic condition and an extremely small part of the patients have tendency to violence. These patients, often teenage, whose thinking and talking are in a mess, may manifest soliloquy, present a kind of through, passion and sensation away from reality and may have paranoia of being persecuted. If not treated early, it may develop into the severer types of psychosis such as schizophrenia or mania. If the patient had been attacked by chronic hepatitis but systemic TCM therapy was instituted in time, clinical psychotic symptoms like disorder of thought may be alleviated. |
|
| Introduction of cases
Case 1 Yang, female, age 36 years. She first visited the clinic in October 1994 with the complaint of pregnancy for 2 more months associated with frequent vomiting, occasional cough, repeated epistaxis and constipation. Physical examination: shrinkage of liver to 4.5 cm. above costal margin. She took 12 parcels of TCM drugs and the symptoms disappeared. She had a return visit 3 months later and was found to have hepatomgaly of 1.5 cm. After taking 15 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver was normal and another 10 parcels were taken before cessation of medication. In June, 1995, she delivered a female baby. At four months postpartum, she made a return visit because of depression and frequent insomnia, fatigue, vertigo, anxiety, distension of abdomen, repeated cough with abundant sputum. Her lower lips showed varicella because of hypersensitivity and she also had pruritus of the above region. Western medical drugs did not show effectiveness. The diagnosis was chronic hepatitis, urticaria, postpartum depression, with TCM classification of liver stagnation and lung dryness. Physical examination: tongue coating yellowish, skin of lower jaw slightly red maculopapular eruptions with urticarial appearance, hepatomegaly of 1.5 cm, percussion tenderness of hepatic region. After taking 6 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver returned to normal, the symptoms disappeared and the skin was normal. TCM drugs were continued for four weeks, at the end of which clinical cure was obtained. The patient was followed up after stoppage of treatment.
|
|
| Case 2
Lai, female, age 47 years. First visit: December 2002. Her husband was a carrier of type A hepatitis virus. Her blood examination showed positive type B hepatitis antibodies. Her body status was of the weak type; she was susceptible exopathy and had excessive sputum. Her cough was severe and spasmodic and caused occasionally a vertigo like sensation. In the recent two years, her emotion was unstable; she had flush, dryness of throat, edema, insomnia, pruritus vulva, leukorrhagia and nocturnal perspiration. She was diagnosed by specialists as emotional disease and was given long term anti-depression drugs. Physical examination: hepatomegaly of 3 cm, (+++) pitting edema of lower extremities. The diagnosis was liver stagnation and lung dryness, wetness-heat vaporization, chronic hepatitis, hepatic psychoneurotic disease. When 3 parcels of TCM drugs were taken abdominal pain and diarrhea occurred thrice a day; cough and sputum decreased. Her body weight decreased and the liver was normal. Edema greatly regressed. After another 3 parcels of TCM drugs, there was occasional abdominal pain and diarrhea was still thrice a day. There was still some coughing but sorethroat and sputum lessened and sleeping was well. Anti-depression drugs were stopped but she woke up early. Bowel movements were normal. Continuation of TCM drugs resulted in disappearance of edema of lower limbs. She slept well and could fall into sleep again shortly after wakening. After taking 10 parcels of TCM drugs, her body weight reduced 5 lbs. Menstruation appeared at the fourth week of medication, the amount decreased but clots were present and the menses persisted for nearly four days. She no longer experienced fatigue. She completed a TCM course of four weeks, by that time she achieved clinical cure and was followed up. |
|
| Case 3
Tsang, female, age 36 years. She made her first visit in April, 1998 with the complaint that she received thyroid operation for hyperthyroidism 10 more years ago. During this period she suffered from severe insomnia, sleeping for only 3 hours a night. She was susceptible to attacks of common cold, palpitation, tremor of hands, sensation of foreign body in the throat. Sleeping pills and anti-depression drugs were of no avail. She had an abortion a year ago followed by repeated secretion of milk in both breasts. Physical examination: hepatomegaly of 3 cm, (+) edema of lower extremities. The diagnosis was chronic hepatitis, hepatic psychoneurotic disease, hepatopathic upper respiratory tract infection, disorder of menstruation, hepatic edema, hepatogenic sexual hormone disorder, hyperthyroidism. After taking 3 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver was normal. At the completion of a TCM therapeutic course, she obtained clinical cure. |
|
| Case 4
Au, female, age 40 years. First visit: December 2000. She complained that since delivery of a female infant, she suffered from postpartum depression; she had mental stress, palpitation, anxiety, insomnia as well as dreamfulness. She had bilateral hypochondriac pain, tiredness of shoulders and back and sensation of a sound ringing in the head (especially during sleep). She now had swelling and pain of the gingivae, belching, chest and hypochondriac pain, increase of white hairs and flush of face. Repeated WM and TCM treatment showed no effectiveness. Physical examination: flush of face, tenderness over right second sternacostal articulation, hepatomegaly of 3 cm, (±) edema of extremities. The diagnosis was chronic hepatitis with TCM classification of flaring up liver yang, deficiency of both liver and kidney, postpartum depression. After taking 3 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver was normal. Her sleeping improved but flushes of face and anxiety and hypochondriac pain was present. During TCM drug administration, there was still some mental stress associated with bitterness of taste. Two weeks later, flush of face disappeared and sleeping was good. At her return visit the symptoms disappeared besides slight shoulder and hypochondriac pain. Menstruation occurred, the amount slight increased with some clots. Physical examination: local tenderness over left shoulder and right second stern costal articulation, liver normal. At the 4th week of therapy, she suffered from diarrhea before sleep for several days; the stools were watery, one to three times a day. A total of 48 parcels of TCM drugs were taken and it brought her the result of clinical cure. The patient was followed up. |
|
|
By WONG Kwok Hung Published on 30th January 2003 Translated by Professor Zheng in June 2005 |
Hepatic psychoneurosis (Part 3)
|
Preface Nervous system damage and psychotic disturbance following liver disease may occur simultaneously or one after another, their clinical manifestations complicated and varied. From the viewpoint of TCM, consciousness and mental condition are closely related to liver. There was an old saying: “Seven emotions and six desires” can hurt the liver. Clinical cases indicate that this is true. The author encountered two sisters with chronic hepatitis who had obtained clinical cure but both had relapse of disease because of their mother’s critical illness and also another case with clinically cured cirrhosis of liver who had relapse of disease following the run away of his wife and daughter. They were all cured through administration of TCM drugs. Review of TCM theory concerning origin of disease give us a clear understanding that “liver disease” is an important origin of “psychoneurotic disease” symptoms.
|
|
| Etiology and pathogenesis
In liver disease, the underlying pathogenesis is related to the attack of “pestilential toxic evil” which causes the flaring up of heart fire, liver fire and kidney fire as well as the heat of large intestines, forming symptoms of different systems in different periods of life. Prolonged consumption of would certainly produce deficiency of liver and kidney. In this aspect, ancient medical literature had many penetrating views, e.g.: |
|
|
|
| It is not hard to find that TCM treatment of neural and psychotic diseases, often starts with “soothing liver and eliminating stagnation” and has achieved brilliant results. Under the direction of this concept, our centre takes advantage of this concept to examine the presence of abnormal margin of liver dullness in order to determine the existence of liver damage. After using several parcels of TCM drugs, the liver usually can return to normal, by which time, the liver function is improved and the psychoneurotic symptoms can often be rapidly abolished. Of course, such “treatment from the fundamental” is better than taking sleeping pill. | |
| The clinical manifestations of psychoneurosis are closely related to degree of damage to visceral organs induced by “liver disease” Liver disease develops during infancy and childhood; if clinical cure is not achieved through effective systemic TCM treatment, the disease would be carried along the entire life time of an individual. At different stages of life, the disease progresses “from superficial to deep, from exterior to interior” and its clinical symptoms are manifested as those described in the forms classified by TCM for chronic hepatitis. Therefore, in certain periods of life, the psychoneurotic symptoms may differ in accordance with the degree of liver function damage and express itself as certain forms of psychoneurotic disease. These conditions include not only those mentioned above: neurasthenia and climacteric syndrome, but also depression, postpartum depression, schizophrenia, disturbance of autonomic nervous system, migraine, internal ear vertigo(imbalance of auricular fluid), hepatic neural disease, etc; all these are psychoneurotic complications seen after liver disease. Since the disease comes from damage of hepatic function, administration of effective systemic TCM therapy may produce complete cure. |
|
| (1) Hepatopathic autonomic nervous system disturbance
Chronic liver disease patients usually have simultaneous damage of autonomic nervous system and this is more commonly seen in cirrhosis of liver. According to reports, the incidence of hepatopathic autonomic nervous system disturbance is 49%-64%. Previously, autonomic nervous system disturbance was thought to be common in alcoholic liver disease, but recent researches have demonstrated that it is also very common in virus hepatitis. Because autonomic nervous system disturbance causes disorder of hemodynamics, the patient’s heart rate and cardiac output increases, but the blood pressure is low, indicating lowering of peripheral vascular resistance, and so low blood pressure is the symptom frequently encountered. Other symptoms include a rather rapid heart rate, vertigo, abnormal perspiration, difficulty in swallowing, dryness of mouth and eyes, impotence, retention of urine, constipation or diarrhea, and in severe cases, fecal incontinence.
|
|
| Case 1 – positive type B hepatitis virus carrier turns negative
Chan (code number 352), male, age 48 years. First visit in January 1987. He had a history of positive type B hepatitis virus carrier and frequently suffered from common cold, aerophobia and chilliness, sore throat and fever, itching of throat and cough, fatigue and headache, heat and restlessness in five hearts, dryness of mouth and throat, aphthae, constipation, hematochezia, acne, insomnia, pain in hypochondrium, dryness and desquamation of lips, and repeated pain of right knee joint. Physical examination: edema of lower extremities, low blood pressure (82-96/50-60 mm Hg.), show pulse rate (42-60/min), hepatomegaly of 1.5 cm. The diagnosis was chronic hepatitis with TCM classification ofliver stagnation and lung dryness complicated by disturbance of autonomic nervous system. The patient received treatment and observation for ten more years in our clinic, during which time his hepatomegaly relapsed for five times (all 1.5 cm) and every relapse was cured by systemic TCM therapy. Blood examination on 27th February 2001 showed a negative result for type B hepatitis virus.
|
|
| Case 2 – lean, pale looking female with of deficiency of blood and weakness of qi, complicated by disturbance of autonomic nervous system Wang – (code number 528) female, age 19 years. Date of first visit :16th May 1994. She complained that she had a cardiac murmur since childhood and often experienced vertigo, palpitation, low blood pressure and insomnia for 3 to 4 years, and occasionally could fall asleep only at 2-3 AM at night, being dreamful and also wakeful. She also had dryness of throat, thirst, nocturnal drinking, distension of abdomen, poor appetite, constipation alternated with diarrhea, yellowish urine and frequent nocturnal urination. Physical examination: lean, pale looking, pulse 100 per minute, percussion tenderness over hepatic region – hepatomegaly of 3 cm. The diagnosis was hepatomegaly for investigation with TCM classification of deficiency of blood and weakness of qi, complicated by disturbance of autonomic nervous system. After taking two weeks of TCM drugs, her sleeping improved, could sleep 5-6 hours in a night; her mental status was good; the pulse 82/min and the medication was stopped. On 1st September 1994, she made a return visit and her menstruation was in the fourth day with a larger amount and bright red color. She also had palpitation and insomnia. Physical examination revealed a hepatomegaly of 3 cm and pulse 100/min. After 17 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver returned to normal, insomnia disappeared and the mental status remained good. She completed the four week TCM treatment, achieved clinical cure and was fallowed up after cessation of therapy. |
|
| (2) Hepatic neurosis
According to reports, about 10% chronic active hepatitis patients would develop hepatic neurosis, such as acute multiple radiculoneuritis, multiple peripheral neuritis and cranial nerve palsy. In the 3048 cases with abnormal margin of liver dullness treated in our centre, 129 cases (amounting to 4.23%) have symptoms of hepatic peripheral nerve disease, in which, female 96:1954 = 4.91%, male 33:1094 = 3%. These cases include trigeminal neuralgia, sciatica, intercostals neuralgia, multiple neuritis, facial neuritis.
|
|
| Case 3
Lee (code number 2115), female, age 70 years. First visit: April 2000. She complained of long time insomnia, palpitation, fatigue and weakness of lower limbs, feverish sensation in the chest, palms and soles, restlessness and frequent nocturia as many as 5-6 times a night. Last years, left trigeminalgia persisted for several months leading to marked emaciation. Relapse of neuralgia now induced insomnia, distension of abdomen, left loin pain and frequent urination. She had been operated on uterine myoma and appendicitis. Physical examination: lean, anomaly of hypochondria, percussion tenderness over hepatic region, hepatomegaly of 3 cm, (+) edema of lower extremities. The diagnosis was hepatomegaly for investigation, hepatic neurasthenia, hepatic neural disease (fifth cranial nerve).
During TCM therapy, she had abdominal pain, diarrhea, large amount of stools, but after the second parcel of TCM drugs, neuralgia subsided and she could sleep well; her emotions calmed down. She had no palpitation and nocturia ceased; the margin of hepatic dullness was normal. Another 3 parcels resulted in good sleeping, abdominal distension and loin pain disappeared and bowl movements occurred every other day. She did not feel any discomfort; the blood pressure was 160/86 mm Hg. She completed the four week course of TCM therapy, at which time clinical cure was obtained and treatment was stopped. |
|
|
(3) Auditory vertigo (imbalance of auricular fluid)
Previously, the etiology of this disease was considered not clear. But recently, it is acknowledged that the course may be functional disturbance of autonomic nervous system leading to edema of labyrinth of internal ear. The typical symptoms are paroxysmal vertigo associated with tinnitus and disturbance of hearing. The attack is sudden; the sensation is spinning of surrounding things usually associated with nausea, vomiting paleness of face, perspiration and lying on bed with eyes shut, daring not to move a little bit. In our 3048 cases of abnormal margin of liver dullness, 116 cases have symptoms of auditory vertigo (3.81%) in which female 93: 1954 = 4.75%, male 23:1094 = 2.1%. |
|
| Case 4
Cheung(code number 237) male, age 48 years. His first visit was on 21 January 1997. He had an appendectomy in 1976, and was examined to have type A hepatitis antibodies; he was given type B hepatitis preventive injection. Four months ago, blood examination showed abnormal liver function and high ferment, and there was no special treatment in western medicine. In the recent 3 months, he had repeated vertigo, vomiting and was hospitalized on one occasion for severe vomiting and vertigo. He was treated with WM drugs and physiotherapy but of no avail; now the attacks repeatedly occurred but the time was transient. In the past, he often felt tired and had generalized pain of bones, yellowish urine, poor appetite, palpitation, insomnia, pain over hypochondrium and frequent nocturia. Physical examination: pulse 104/min, dryness, desquamation and scaly appearance of skin of abdomen and lower extremities, tongue enlarged with teeth prints, abdomen distended, percussion tenderness over hepatic region, hepatomegaly of 1.5 cm, (+) edema of lower extremities. After taking 13 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver was normal. During systemic treatment, vertigo disappeared. The patient was treated and followed up for many years in our centre and for five more years no relapse of vertigo was seen. |
|
| (4) Migraine
Migraine was previously considered as a disease of unknown etiology. It is more common in females and it usually begins in adolescence and manifests cyclic attacks. Migraine is in fact a kind of functional disturbance of vascular contraction and relaxation which leads to paroxysmal headache. The attack is usually associated with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, intestinal gurgling, perspiration, constipation, diarrhea, photophobia and numbness of limbs. After attack, the patient often feels tired and sleepy. In female patients the attack of migraine is often related closely to menstrual blood loss. In the 3048 cases of abnormal margin of percussion dullness of liver in our centre, 160 cases (5.25%) have migraine symptoms, in which female 126:1954=6.4%, male 33:1094=3%. In female chronic hepatitis patients, migraine attacks usually occur before or after menstruation. In some of these cases, attacks are likely to occur when these patients had repeated postmenstrual blood loss (blood deficiency headache: deficiency of blood causes deprivation of nourishment of brain, a condition susceptible to invasion of wind evil and turbid air leading to headache). |
|
| Case 5
Chan (code number 293) male, age 55 years. His first visit was on 10th October 1993 with the chief complaint of repeated hypertension, migraine, neurodermatitis and hemorrhoids for several decades and treatment was of no avail. He had received hemorrhoidectomy, appendectomy and sebacious cyst excision of the back. Physical examination: hepatomegaly of 4.5 cm. The diagnosis was hepatomegaly for investigation with TCM classification of blockage of channels and stasis of blood and excess of liver yang associated with migraine. After treatment with systemic TCM drugs, the symptoms were under control to a marked degree and the anti-hypertension drugs taken for a long time were stopped; dermal pruritus and migraine disappeared. Hemorrhridal sufferings had markedly decreased. He was followed up for nearly ten years and took TCM drug occasionally. |
|
| Case 6
Shu (code number 024) female, age 27 years. First visit: September 1992. She gave birth to a female infant one year ago and thereafter, she often felt tired and had also vertigo, sleepiness, abundance of sputum and distension of abdomen which was more marked after meal. The skin was susceptible to ecchymosis and brushing of teeth often induced bleeding of gums. Her menstruation was usually overtime. Physical examination revealed an anemic looking, a soft abdomen with tympanites, shrinkage of liver margin, the lower limit 4.5 cm above costal margin and (+) edema of lower extremities. After TCM treatment for 11 days, the liver returned to normal and clinical cure was obtained after systemic TCM therapy. The patient was followed up after cessation of treatment. In May, 1994, she had a return visit, complaining of paroxysmal migraine and when severe, radiating to the neck with simultaneous association of lacrimation and excessive nasal discharge. If the attack is at night, the patient might be awakened by the pain. Western medical drugs did not show effectiveness. Physical examination: hepatomegaly of 3 cm with percussion tenderness. After taking 10 parcels of systemic TCM drugs, the liver was normal and migraine disappeared. The treatment persisted for another 4 weeks and was stopped. Five weeks of follow-up did not show any abnormality. |
|
| Case 7
Tong (code number 2546) female, age 45 years. First visit: June 2001. She complained of right side migraine for 20 more years. She had history of gastric illness and rather severe hemorrhoids with hematochezia. She also had (±) edema of lower limbs, hepatomegaly of 3 cm and percussion dullness over splenic region. The diagnosis was hepatomegaly for investigation with TCM classification of wetness-heat vaporization, blockage of channels and stasis of blood complicated with migraine. After taking 3 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver was normal, the splenic dullness was present and the right side migraine decreased in severity. There was flatulence, dermal pruritus and red eruptions. After another 3 parcels, the persisting time of migraine attack was markedly shortened, but there was still vertigo. The headache gradually subsided during the continuation of TCM treatment. Her sleeping was poor and some pain was present in the tongue. The splenic dullness disappeared. Four weeks later, the dermal pruritius disappeared, her appetite and sleeping was good, no migraine occurred but there was occasional vertigo. She completed her 6 week systemic TCM course of treatment and was followed up. |
|
|
By WONG Kwok Hung Published on 30th January 2003 Translated by Professor Zheng in June 2005 |
Hepatic psychoneurosis (Part 2)
| Preface
Strenuous urban life causes neurasthenia of the Hong Kong people; they are also susceptible to nervousness, mental fatigue, depression and insomnia. TCM principle bases on the balance of yin and yangand considers that the physiologic role of liver is chiefly smoothing and regulating and storage of blood. It is on this basis that TCM analyses hepatogenic psychoneurosis. The symptoms of hepatogenic psychoneurosis are widely encountered. Liver disease patients with impairment of liver function have a 65% incidence of central nervous system damage; the cause is chronic hepatitis after infection by hepatophitic virus and this is also the fundamental cause of peripheral nervous disease and psychosis which are frequently seen in clinical practice. Early in the beginning of 19th century, scholars reported that nervous system complication occurred in virus hepatitis and cirrhosis of liver. Although the pathogenesis of hepatic psychoneurosis is not clear, yet modern medical research has confirmed that “injury of autoimmune function, lack of vitamin B complex or impairment of liver function can cause inability of detoxication and elimination of toxic material”; these conditions can cause damage to brain and nervous tissues. The course of hepatogenic encephalopathy may be acute or chronic, its clinical manifestation may be mild or severe. Severe cases of hepatic encephalopathy often present manifestations of acute liver disease which includes symptoms of mental confusion (confusion of consciousness, taciturnity, depression or joyfulness, polylogia, hyperactivity, excitability and mania, or passing into disturbance of consciousness or even hepatic coma) and dyskinesia (flutter-fibrillation). The severe cases that have to be treated immediately in hospital are not mentioned here, but it should be emphasized that the danger of becoming chronic hepatitis by hepatophilic virus infection must be made clear to everyone and it must be treated at the stage of “chronic hepatitis’ with effective systemic TCM therapy in order to prevent damage to the brain and nervous tissues. As to the cases belonging to “subclinical hepatic encephalopathy”, the patients may show no psychoneurotic symptoms after the hepatitis attack, their routine psychotic and nervous system examinations are also normal, but with intellectual or psycho logic monitoring, abnormality demonstrating encephalic atrophy may be found following long term liver disease. According to statistics, the incidence of subliminal hepatic encephalopathy is 60% in cirrhosis of liver. Due to lowering of intelligence and ability of decision, the individual is extremely susceptible to traffic accident if he is a driver; therefore, if the disease is discovered early and treated in time, accidents may be avoided. In addition, chronic hepato-encephalic degeneration is often seen in male patients with cirrhosis of liver, presenting, in the early stage, psychoneurotic symptoms such as tremor of fingers, dysphonia, slowness and monotony of speech, unclear enunciation, tremulous and involuntary movements. It may also show intellectual disturbance and paroxysmal disturbance of consciousness (mild cases showing haziness, severe cases coma persisting several hours to several days and attacks occurring once in two weeks or several times in one week) associated with flutter-fibrillation and stiffness of muscles. If consciousness recovers, the symptoms may be relieved (folks regard this condition as the body occupied by ghost). If treatment does not aim at the primary liver disease and at protection of the liver, the patient would gradually show infantile disposition, apparent thinness, contracture of limbs, and degeneration of mental function. It was said that from mental degeneration to death, the time may be 1-2 years (the course may be 8 months in sub-acute cases and more than 6 years in chronic cases). In late cases of hepatogenic psychoneurosis, no doubt, treatment is difficult, but one should not forget that early diagnosis and treatment of liver disease can prevent the progression of disease into hepato-encephalic degeneration. Hepatophilic virus infection is extremely common. “China has 50 million people suffering from various kinds of brain diseases”. “Cerebral palsy has an incidence of 18.4% in the population, week-minded children occupying 22.2%, senile encephalopathy having an incidence of 10% in the elderly population” (seen in 19th November, 2002 Ta Kung Pao – Special Topics). According to the above figures, we cannot estimate yet how many of them are the result of “hepatophilic virus” infection. However, clinical practice has demonstrated that in the early stage of chronic hepatitis, treatment of psychoneurotic symptoms with TCM drugs gives immediate effectiveness. TCM drugs can effectively eliminate antigen-antibody complex, relieve edema, improve microcirculation of encephalic nervous tissues, recover hepatic function and can further abolish disturbances of metabolism, excrete retained noxious metabolic materials, and increase activity of nerve cells. In the course of life time, the individual might have been repeatedly infected by hepatophilic virus within the maternal body or during infancy. When the individual is ascertained to have “chronic hepatitis”, various symptoms of different forms of chronic hepatitis may display during different periods of life and different clinical symptoms of psychoneurosis may manifest. It is only during different periods, according to commonly seen symptoms, that people consider it as a kind of disease. It is unfortunate that some physicians as well as patients do not understand that its origin is related to hepatophilic virus infection and its consequence, chronic hepatitis. Because of such misunderstanding, one would let the chance of fundamental treatment slip by. The following common diseases are in fact hepatogenic psychoneurosis related to chronic hepatitis. |
|
| “Post-hepatitis syndrome” and “Hepatic disease syndrome”
As early as 1944, scholars suggested that patients who had been attacked by acute hepatitis but whose liver function or even liver biopsy was normal still presented subjective symptoms, this condition should be called “post-hepatitis syndrome”. In the recent thirty years, because of the understanding of the complexity of chronic form of type B, type C hepatitis and the difficulty of differentiating “post hepatitis syndrome” from chronic persistent hepatitis, this term is rarely used now. Clinically some patients although devoid of history of acute hepatitis, may have no abnormality of liver function. But, still, there are quite a number of patients presenting the five main symptoms of “post-hepatitis syndrome”: abnormal margin of percussion dullness of hepatic region, edema of lips, tongue and hypochondria of various degrees, prominence of veins, and percussion tenderness of hepatic region. The five main symptoms are:
In fact, people previously considered that “post-hepatitis syndrome” was usually seen among intellectuals and medical workers due to their mental overload and worriness about liver disease. But now, according to clinical observation, “ post-hepatitis syndrome” patients are actually chronic “hepatophilic virus disease” patients whom are disseminated widely and usually found to have signs and symptoms of chronic hepatitis and most of them are suffering from a disease during activation. Though several decades of investigation, the diagnosis of chronic hepatitis was standardized according to the results of laboratory examination, type B ultrasound and computer scan. But the dependence on the latter items was over emphasized and this caused the loss of opportunity of early diagnosis in many patients. The existence of these “post-hepatitis syndrome” patients is an objective matter, therefore, the term “liver disease syndrome” is more appropriate. Clinical practice has demonstrated that TCM drugs yield ideal results in these patients. |
|
| Climacteric syndrome
Climacteric syndrome refers to disorder of autonomic nervous system caused by fluctuation or lowering of estrogenic hormones before or after menopause or loss of ovarian function after surgical excision or radio therapy. From the TCM viewpoint, it is caused by regression of kidney qi or imbalance of yin and yang of the body. Quite a number of female patients had been infected by hepatophilic virus originally and had different degrees of endocrine disorder in early years, so that when they passed into the climacteric stage, the symptoms of excessive yang became apparent. When ovarian function decreases and disturbance of autonomic nervous system appears, somewhat prominent climacteric symptoms may appear as the individual passes into the pre-climacteric or climacteric years. Therefore, the existence of “abnormal margin of liver dullness” often becomes one of the criteria of diagnosing simple climacteric syndrome. So, when patients with abnormal margin of hepatic dullness have climacteric symptoms, such as hypertension, repeated migraine, menorrhagia, varicosities of lower limbs, glomerulate telangiectasis and hepatic edema, simple hormonal treatment should be avoided and effective systemic TCM therapy should be applied. In such a way, climacteric symptoms would subside by using less effort and result in greater effectiveness.
|
|
| Introduction of cases
Case 1: Wong (code number 097), female, age 30 years. Her mother had carcinoma of liver and died in 1997. One year later, she had blood examination and was found to be a carrier of type B hepatitis virus. At the first visit in September 1998, she complained of fatigue and sleepiness, palpitation, insomnia, pain of shoulders and neck and repeated right hypochondriac pain. She often experienced loss of appetite, aphthae belching, abdominal distension, tenesmus, abdominal pain, diarrhea and she had history of hemorrhoids. She had menorrhagia with numerous blood clots and dysmenorrheal. Body weight: 46 kg. Height :1.62 m. BMI: 17.69. Physical examination: BP 80/60 mmhg, tongue red with numerous teeth prints, tenderness over both hypochondria, hepatomegaly of 3 cm. The diagnosis was “liver disease syndrome”. After taking 3 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver reduced 1.5 cm and after another 3 parcels, it was normal. The symptoms subsided and insomnia disappeared. But she stopped the TCM drugs by herself after taking only 15 parcels. She made return visits later, one at the end of 1998 and another at the beginning of 1999, with a hepatomegaly of 1.5 cm and 3 cm respectively, but systemic TCM therapy was not administered. Afterwards, a return visit was made in March, 2000, when she complained of fatigue, constipation, hematochezia, repeated exopathic headache, cough, insomnia, deep yellowish urine and a hepatomegaly of 3 cm. After 3 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver returned to normal. The systemic TCM therapy continued for 4 weeks and was stopped after achievement of clinical cure. |
|
|
Case 2. Yang — (code number186), female, age 55 years.
Her first visit was in December 1994. She had cholecystectomy in 1980 due to bladder stones and complained of suffering frequently from insomnia, flush, anxiety, depression, dermal pruritus, fatigue, vertigo, headache, loin and abdominal pain, alternation of diarrhea and constipation and defecation right after meal.
Physical examination: percussion tenderness over hepatic region, hepatomegaly of 3 cm, (+) pitting edema of lower extremities. She was diagnosed as neurosis and climacteric syndrome. Repeated TCM and WM treatment did not show effectiveness. She came to our centre and was diagnosed as chronic hepatophilic virus disease with wetness-heat vaporization, deficiency of blood and weakness of qi forms; hepatogenic malnutrition. After taking 18 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver was normal and the symptoms disappeared. Following 4 weeks of systemic TCM therapy, clinical cure was achieved and the climacteric symptoms disappeared. She was followed up after cessation of TCM drugs. Four years later, she had a return visit because of insomnia for 2 weeks associated with fatigue, vertigo, headache, loin pain, she was afraid of relapse of the liver disease. Physical examination revealed a hepatomegaly of 3 cm, percussion tenderness over hepatic region and (+) edema of lower extremities. TCM therapy was administered and after 3 parcels, the liver returned to normal and the symptoms subsided. Continuation of TCM therapy for 2 weeks ended in disappearance of symptoms and afterwards she stopped the medication. |
|
|
By WONG Kwok Hung
Published on 28th November 2002 Translated by Professor Zheng in April 2004 |
Hepatic psychoneurosis (Part 1)
|
Preface Urban life is full of stress, therefore, Hongkong people are susceptible to neurosis, nervousness, mental fatigue, depression and insomnia. The basis of TCM is to balance yin and yang; it concentrates on the liver because it has the function of smoothing and regulating the flow of vital energy and blood. Analysis of hepatogenic psychoneurosis caused by liver disease is helpful for the understanding of clinical diseases such as hepatogenic psychoneurosis, hepatogenic neurosis (including neurasthenia, disorder of thought, obsession) hepatogenic autonomic nervous system disorder and hepatic complications that lead to climacteric symptoms, postpartum depression and sub clinical hepato-encephalopathy. Hepatic neurosis are closely related to liver diseases; when liver disease is treated with effective systemic TCM therapy, the hepatogenic psychoneurotic symptoms are also relieved and the disease may be cured at the same time. The concept that “hepatogenic virus is the origin of many diseases” may not be accepted by many people, but the experience of our several decades of clinical practice makes us believe that this may be the truth which is worthwhile to be introduced to the community. In the past, a great deal of professional knowledge (including medical knowledge) were monopolized and people were often unable to have the knowledge that they should have and no matter from whom they received treatment, whether TCM or WM, the treatment they could have was symptomatic, that is, “treat the head when the pain is in the head.” In fact, quite a number of previous issues written by specialists had contents about “liver disease”; they introduced that “hepatophilic virus” could damage many systems of the human body causing functional impairment and consequent development of different disease in which chronic hepatitis with psychoneurotic symptoms occupied not a small amount. This article introduces this kind of hepatitis with “psychoneurotic” symptoms to people for the understanding of the relation between “psychoneurotic” symptoms and acute or chronic hepatitis. If the patients know that the psychoneurotic symptoms originate from “chronic hepatitis”, they would naturally “seek for the fundamental” in treatment. If one goes “to treat the liver” from the fundamental, probably clinical cure can be attained. |
|
| TCM theory on liver disease
According to the physiologic function of liver which is based on TCM principle, it is not difficult to understand the affection of liver disease on human psychoneurologic system. From the TCM viewpoint in reorganization of disease, the disorder of zang and fu organs is closely related to the symptoms of mentality. In general, the pathogenesis of chronic liver disease, affected by pestilential evil, may lead to the production of heart fire, liver fire, abundance of lung fire and flaring up of large intestine heat. When hepatic storage of blood is impaired, heart disease is produced, and the “storage of spirit in heart” is frustrated; the result is the appearance of symptoms like palpitation, insomnia, dreamfulness, endless crying or laughing, delirium or idleness, sleepiness, indifference, pain or heaviness over pericardial region, face and nails showing pale or purplish color, in severe cases, coma may be the consequence. In addition, if stagnation of liver qi and uprising of liver yang occur in liver disease, the following symptoms may take place: vertigo (眩暈目花), pain at top of head, distension of breasts, pain over costal region, lower abdominal pain, unsmooth mobility of joints , clonic spasm of muscle (筋攣拘急), numbness limbs (四肢痳木), impotence (急燥), irritability (易怒) and convulsions (抽搐). If kidney water is consumed due to prolonged excessive fire of heart, liver and kidney, weakness of kidney is prone to occur and it would further lead to deficiency of yin and increase of fire. The TCM theory acknowledges that kidney has the function of concentration and remembrance and inability to concentrate the mind and loss of memory are common symptoms in hypofunction of the kidney. Kidney is responsible for memory, fear and fright. Fear is conscious and is ordinarily called timidness, being in a particular mental state fearful of something; while fright is unconscious and is a mental state caused by the sudden occurrences of something. Although fear and fright both belong to kidney, but they are also closely related to heart which stores spirit and to liver which stores blood. Therefore, when there is deficiency of yinand abundance of fire and uprising of liver yang, aysphoria with feverish sensation occurs in chest, palms and soles, the face and ear are red, the lips, tongue and throat are dry, the patient feels thirsty and has to drink nocturnally, the oral taste is bitter and the urine yellowish, the tongue coating thick and dark in color, the tongue proper scarlet red with pricks and ecchymoses, pigmentation appears on the face, back of hand, forearm and abdominal wall (the common sayings are freckle, senile plague, liver plague). In severe cases, there may be anarsaca, difficult mobility, hypertension, frequent nocturia and wakefulness.
In fact, the functions of heart, liver and kidney are closely related so that when the body is invaded by pestilential evil (hepatophilic virus), the functions of zang and fu organs can affect one another and it is not surprising that various psychoneurotic symptoms occur. It is unfortunate that modern medicine “separates apart” the wholism concept of disease and goes after only the micro-pathological changes but neglects the TCM “concept of wholism”. Therefore, the patient loses his right “to be treated from the fundamental” and medical research might be easily directed to the wrong path.
|
|
|
TCM concept acknowledges that liver is “the location of spirit, the store of blood, the origin of tendon”. The chief physiologic functions of liver are regulation of the flow of vital energy and storage of blood. “Su Wen” (“Plain Questions” (《素問》) had pointed out :”Liver is an organ of the character of a general who does the planning and thinking”; “Liver is the fundamental of regulation and the location of spirit”. Therefore, besides regulation of vital energy and promotion of the digestive function of spleen and stomache, the liver can regulate emotion.
If the smoothing and regulating function of liver is normal, vital energy is smooth, qi and blood are in harmony and the individual is in high spirits. If the smoothing and regulating function is impaired, the liver qiis stagnated, emotion is depressed, and the individual is susceptible to irritation. Sometimes, the flow of vital energy in liver is excessive, yang qi flares up, emotion is easily irritated and the individual is susceptible to anger. Therefore, “Su Wen” stated: “In the liver disease patient, both hypochondria are painful; the pain spreads to the lower abdomen and the individual becomes angry easily”. |
|
|
Liver stores blood; it also regulates blood. If the function of blood storage in liver is normal, the spirit has its house; if the mental regulatory function of heart is normal, there is a feeling of high spirits, the hearing is clear, the thinking is nimble and the response is quick. If the liver blood is insufficient and the blood in the heart is consumed, the spirit can not dwell in the house, so that the individual is often wakened up by horrible dreams, can not sleep well, and has sleep-walking, nightmare and delusions. Therefore, when there is liver disease, its function of storage of blood is impaired, not only deficiency of blood or hemorrhage is induced, but also the qi of the heart is insufficient, blood is consumed, the blood vessels are not patient and the blood flow is not smooth, These factors affect the heart to hold the spirit and when this function is abnormal, (i.e. the physiologic function of the human brain such as mentality, consciousness, thought), there will be insomnia, dreamfulness, mental instability, delirium or sluggish response, amnesia, listlessness or even coma. At the same time, pathological changes due to insufficient blood supply may be induced, such as insufficient qi and blood in liver, weakness of tendons and muscles and unsmooth mobility due to insufficient nutrition. If liveryin is insufficient, the patient may show tremor and numbness of limbs and unsmooth extension and flexion of the extremities. |
|
|
Very close relation between liver disease and psychoneurotic disease The relation between “liver disease” and “psychoneurotic disease” is very close. In the present state of medical research, although investigations show that liver disease can induce simultaneously or secondary damage of the nervous system and psychotic symptoms, so far, no definite and unanimous classification has been advanced. In fact, when there is acute infection of the human body by hepatophilic virus, the patient may also have the chance to be attacked by hepatic encephalopathy, hepatic coma, hepatic neurosis, brain edema or even meningitis, epilepsy, acute transverse myelitis, and multiple sclerosis. In severe cases, when multiple organs are damaged due to hepatic encephalopathy, the mortality rate may exceed 77%. Hepatophilic virus infection causes extensive damage to many systems of the body. Therefore, patients with this acute and serious disease should be hospitalized early and receive emergency treatment immediately. The damage of nervous system and appearance of psychotic symptoms induced by liver disease may occur simultaneously or one after another or only one of them may appear. But, if the liver disease is prolonged or if damage of liver function is severe, and the disease has progressed into the stage of cirrhosis, the clinical psychoneurotic symptoms gradually would become apparent and the patient would progress into hepatic coma. In the patients who clinically have manifestations of “deficiency of blood and weakness of qi” form of TCM chronic hepatitis, not a few have psychoneurotic symptoms and often they are diagnosed as having neurosis or other psychoneurotic diseases. In the active chronic hepatitis patients (especially common in virus or alcoholic liver diseases), about 10% may develop hepatic neurosis; their peripheral neural symptoms usually appear at the late stage of liver disease (a part may appear at early stage) and these symptoms may become the chief cause of visit to the clinic. |
|
| Hepatogenic neurasthenia (肝源性神經衰弱)
We provide particularly the following introduction because neurosis as a complication in the early stage of liver disease is extremely common. The statistic of our centre shows that in 3001 cases with abnormal margin of hepatic dullness, 557 cases have manifestations of “neurasthenia”, occupying 18.6%. In 1930 female cases, 416 have “neurasthenia”, occupying 21.6%; in 1071 male cases, only 141 have such suffering, occupying 13.2%. It is clear that neurasthenia in females has a higher incidence than male and this may be ascribed to the physiologic function of the female body which is prone to develop “deficiency of the blood in the heart” that promotes the symptoms of “neurasthenia”: Clinically, neurasthenia is one of the most common functional diseases of neurosis; the symptoms of this entity are numerous, their manifestations chiefly are the following:
|
|
Introduction of casesCase 1 Yang (code number 2011) female, age 49 years. Date of first visit: 18th December 1999. Her husband had history of hospitalization for acute type A hepatitis. She complained that she had insomnia for 20 years and she had to depend on hypnotics. She suffered at times from loin pain, tiredness and sleepiness. She had constipation and abdominal pain since the age of 20 and often had to take cathartics to promote bowel movements. She had hemorrhoids and hematochezia and had received hemorrhoidal operation. She experienced repeated numbness of limbs and spasm of lower extremity muscles and also frequency of urination. Her irregular menstruation was associated with serious dysmenorrheal and her climacteric symptoms became more apparent a year ago. She took continuously contraceptive pills. Physical examination: tongue red with multiple ecchymoses, anomaly of both hypochondria with protrusion of right side, hepatomegaly of 3 cm with percussion tenderness over hepatic region, prominent veins of lower extremities, large glomerulate patches of telangiectasis on right thigh. The diagnosis was deficiency of Qi and weakness of blood associated with wetness-heat vaporization, blockage of channels and stasis of blood, deficiency of both liver and kidney. After taking 2 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver returned to normal. She had received 6 weeks of systemic TCM treatment, during which time she had intermittent passing of wetness-heat stools, burning sensation of anus, tenesmus and prolapse of hemorrhoids; occasionally, she had increase of sputum tinged with blood and also frequency of urination and headache. On the continuation of TCM therapy, symptoms of neurasthenia and climacteric gradually disappeared and she stopped taking the contraceptive pills. |
|
| By WONG Kwok Hung
Published on 31st October 2002 Translated by Professor Zheng in June 2005 |
“Obesity” is an epidemic! — Comments on hepatogenic secondary obesity (Part III)
| Preface
At the present time, the importance of human diseases caused by “hepatophilic virus” is recognized more and more by people. Different places of the world have different types of hepatophilic virus and according to statistics; there are over 320 million people in the world having type B hepatitis. In fact, how many people are infected by the other 6 types of hepatitis virus ? How many people are yet to be confirmed as victims of infection by hepatophilic virus ? It is actually difficult to estimate. The WHO “International obesity working team” pointed out recently, that obesity in human population has spread all over world, in which 750 million are over weight, 300 million suffer from obesity and diseases related to obesity are disseminating. Since, “abnormal obesity” is generally acknowledged as an epidemic, is it then corrects to say that there is no relationship between hepatophilic virus infection and “abnormal obesity”? |
|
| The cause of hepatoginic secondary “obesity” is hepatophilic virus infection
It is beyond doubt that the sequelae of virus hepatitis are “fatty liver”, “hepatic edema” or “hepatogenic secondary obesity”. We must find out the fundamental cause which leads to the development of obesity and take measures to prevent and treat them accordingly. We must not let people indulge in the concept of over nutrition and insufficient physical exercise and let them intermingle “secondary obesity” and “simple obesity”. People should be told to avoid incorrect fat reducing methods and taking fat reducing drugs that hurt the liver. Otherwise, liver disease patients with obesity might have their illness aggravated from “fat reducing”. It is commonly accepted that patients with “abnormal obesity” are prone to develop diseases that might affect health. On the other hand, hepatogenic secondary obesity resulted from “hepatophilic virus infection would be neglected. “Liver disease” itself can produce “abnormal obesity” and the patient becomes susceptible to extra hepatic complications which are commonly seen in obese individuals, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, rectal carcinoma and apoplexy. Therefore, “abnormal obesity” is only one of the sequelae of hepatophilic virus infection and to prevent and treat obesity from the fundamental, one should base on making it known to the public the prevention of “hepatophilic virus” infection and the use of effective systemic TCM therapy. Fat reducing without physician’s direction often would induce adverse results. So, we suggest, that individuals suffering from liver disease or not yet ruled out liver disease, and intending to reduce fat, should consider cautiously the following conditions: |
|
| (1) Confirmed to have been attacked by acute or chronic hepatitis followed by marked increase of body weight and becoming fat afterwards;
(2) Liver function found to be abnormal by blood examination or positive reaction of virus hepatitis antigen and antibody (antibody positive after hepatic vaccine injection excluded); (3) Close relatives or those in close contact with history of virus hepatitis, cirrhosis of liver or carcinoma of liver; close relatives or those in close contact, having positive hepatitis virus surface antigen reaction in blood examination (i.e. virus carrier); (4) Those suffering frequently from diseases and symptoms of chronic hepatitis TCM classification (seen in web page) or those with abnormal margin of hepatic dullness or hepatomegaly diagnosed by ultrasound or CT scan; (5) Those having history of excessive acute or chronic loss of blood, due to serious diseases, delivery or operation (including menorrhagia, gastric bleeding, hemorrhoidal bleeding and traumatic blood loss) and gradually becoming fat afterwards especially those having blood transfusion; (6) Those having been treated for a comparatively long time with steroid drugs because of disease (such as rheumatism, asthma, gout) and gradually developed obesity after a short time of significant increase of body weight; (7) Alcohol or narcotics addiction (especially use of injection syringe in common with others) or prolonged use of drugs harmful to the liver (such as prolonged use of bisatin in chronic constipation); (8) Homosexuals or those suffering from AIDS. Anyone who has one of the above conditions should not undergo fat reducing with drugs. Food control or increase of physical exercise can be done only when liver disease is ruled out so as to avoid the adverse result of malnutrition and more enthusiasm on fat reducing would make more fat deposition and finally, the health condition would be affected.
|
|
|
Methods of fat reducing in patients with “hepatogenic obesity” “Control food intake and adequate physical exercise” is the only scientific method of fat reducing. But the premise is that liver disease must be treated, the progressive inflammatory process of chronic hepatitis must be terminated and the liver function improved. Therefore, the method of first choice to reduce fat in hepatogenic secondary obesity is early effective systemic TCM therapy to achieve clinical cure of chronic hepatitis. Other important methods are: |
|
| (1) Eat less
Reduce food intake is the chief method of control of calorie intake in reducing fat. It has been demonstrated that if obese individuals are accustomed to a low calorie diet for a long period, their body weight would finally be decreased, despite of not doing physical exercise. But eat less does not mean no eating, especially patients suffering from secondary obesity caused by hepatophilic virus disease, who need particularly more fine quality protein, enough vitamins and adequate amount of minerals. It is only when the patient has a “balanced nutrition”, adequate vitamin and mineral supplements and a project under the direction of physician and maintained with perseverance that the success of fat reducing can be warranted. The reduce fat “at random” and “blindly” is lack of scientific planning and is also devoid of will power and resolution, and the result undoubtedly would be ineffective. Some scholars, therefore, pointed out: “Fat reducing by control of food intake has a failure rate between 50% and 95% and this is absolutely not surprising”. We all know the chief cause of obesity is long term excessive calorie intake. The best fat reducing method in simple obesity is to follow the acknowledged programme, that is, decrease calorie and increase physical exercise. To maintain a steady decrease in calorie intake does not depend on the amount of fat, carbohydrate and protein absorption, but is determined by the amount of caloric taken. So, to ensure health, one shouldhave a diet of adequate proportion, that is, at least 60% glucose, 15% protein and the remaining fat. Certainly, the diet should contain less meat and oil and should include chiefly vegetables, beans, fish and some meat and plant oil and one should have no scruples about sugar. If one believes in fat reducing drugs, folk prescriptions or in forcing oneself to control food or even fasting for the purpose of rapid fat reducing, the result will be dangerous to one’s health or even life. It should be pointed out that prolonged abnormal liver function in hepatogenic obesity patients causes deficiency of protein, imbalance of amino acid contents and insufficient colloidal permeability, therefore, adequate protein amount in the diet is extremely necessary. Clinical observation shows that intake of adequate amount of fat and carbohydrates may be more effective in achieving fitness. There is rumour saying that one can use methods like limitation of starch and meat or alternating the intake of simple meat protein with starch food; but actually these are not correct methods which should not be applied, because these administrations would result in hepatogenic hypoglycemia, hypotension or hypertension and cardiac disease. Some specialists pointed out that many diseases related to obesity are in fact related to interrupted limitation of food intake. Many patients with such limitations have cardiac and diabetic problems more than obese patients without diet limitation (especially the secondary obesity patients caused by liver disease). Specialists from many countries have pointed out: “from the beginning, fat reducing by limitation of food intake is destined to end in failure”. “Limitation of food in the early stage may be effective, but in the long run, only a few individuals can reach the goal; of fat reducing, and on the whole, body weight finally regains.” Therefore, in the course of fat reducing by limitation of food, one should not do it with reluctance, and everything should be done under the direction of physician and at the insurance of body health. In addition, during traveling or under emotional embarrassment, one may eat without control and the body weight may increase gradually; but the increased weight is hard to recover, so one should be very cautious about it. Although, nowadays health food is accepted everywhere with appraisal but with the improvement of economic status of the people, vitamin B group deficiency due to refined food, has become a common phenomenon in the society, especially vitamin B1 deficiency can give rise to beriberi, polyneuritis, increase susceptibility to generalized weakness and puffiness, induce fatigue, marked saging of lower eyelid and edema of lower limbs. It can also cause muscular spasm of fingers, toes and gastrocnemius, soreness and weakness o loin, knees and ankles, inability to walk instantly after standing, repeated paroxysmal sciatica, costal neuralgia and these are the result of vitamin metabolic disorder caused by liver function insufficiency. So, long time supplement of vitamin B1, B6, E and Calcium is necessary. Those having abnormal blood coagulation or decreased platelet count should have prolonged administration of vitamin K4 to normalize the coagulation mechanism; as to patients with recurring aphthae and lip mucosal disease, vitamin B2 supplement is advantageous. Administration of these vitamins and calcium is more important to older patients and long period administration may revive the strength of the lower limbs and prevent walking disability. (2) More locomotion More locomotion causes more consumption of calorie. There are two kinds of locomotion: one is aerobic metabolic locomotive activity, which has significant effect on fat reducing, and another is anaerobic metabolic static locomotion like weight lifting, but its fat reducing effect is not good. Because decrease of body weight or reducing fat requires time, one must be clear about one’s own dietary habit and learn to adapt new dietary habit and take more time to do exercises to consume calories. The programme should be blended into one’s daily life so that health and normal body weight can be maintained. Hepatic obesity patients should proceed to physical training for fat reducing after clinical cure. The patient should increase aerobic physical exercises with perseverance from a lesser amount to more and from lighter items to heavier, but it should be emphasized that one should not begin unless one has the indispensable resolution and patience. Increase of locomotion for a short period with eagerness but of not persevered, would often lead to rapid increase of body weight due to increase of appetite following cessation of physical exercise. (3) Maintenance of body weight is the crux Specialists remind people that some young ladies are overcritical to seek for “bone sensation beauty” and practice fat reducing blindly. This is in fact harmful. It was demonstrated that people with low BMI have a greater mortality rate and also cancer mortality rate than people with normal BMI. Therefore, one must not go too far in fat reducing. Now, some young ladies struggle hard to control food intake for the sake of developing a “model” figure, but as time passes by, they would become sufferers of anorexia, menstrual disorders and amenorrhea. Adolescent female needs adipose tissue by the amount of 17 % of total body weight in order to ensure the appearance of menarche and monthly occurrence of menstruation. It must not be forgotten that lean and weakness can give rise to many diseases and may even jeopardize life. Similarly, a lean figure in the elderly may not be a good thing. Some German nutritionists pointed out that old people at the age of 60-70 years, begin to have muscular atrophy, males developing at the rate of 4% a year and females 6% a year. So they consider that body weight slightly over normal may be more advantageous to health and they acknowledge that “the best scheme is to maintain the body weight”. Some other people acknowledge that “the value of keeping body weight in the normal range is no less than anti-cancer”. The above penetrating opinions are indeed good references for reducing fat. (4) Reducing fat should begin in childhood People infected by hepatophilic virus leading to virus hepatitis are not a small number and most of them are infected early in the infantile period; it is due to the strict standard of diagnosis of liver disease that a certain number of the patients cannot be diagnosed early and treated with effective systemic TCM therapy. Such neglect is especially common inn children, adolescents and young women. Recently, some articles, according to investigation, pointed out that newborn infants who increased body weight rapidly would have obesity when grown up. Some said that obesity patients had increased two times since the sixth decade and the age of the patients became younger. The investigation reviewed 9179 individuals between the year 1957 and 1964 and found that those born comparatively later had their obesity developing speed quicker by 30% as compared with those born earlier. In some countries, more than 30% of the children are obese and 22 million children under 5 years of age have been classified as over weight or too fat. For example, in Africa, the number of obese children is four times of those undernourished. From these data, it not difficult to find that obesity is endangering children’s health and it is undoubtedly a fact that makes people worry. Some people have pointed out that abnormal obesity causes chronic injury to children’s cardiovascular and respiratory function, delays their aerobic growth capacity, motivates in advance the reserve cardiopulmonary function, lowers the health quality, hinders the development of psychotic behavior and suppresses the development of potential energy. In adult age, it is an important risk factor in gradual formation of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, hypertension and cancer in certain sites of the body. The danger of death at a comparatively early age in obese individuals is 1.2 times of the non-obese. These risk factors can hardly be explained by “heredity”, “over nutrition”, “disease of the rich” and “insufficient physical exercise”. It may be more reasonable to ascribe to virus infection, symptoms of extra hepatic complications and abnormal liver function, and it is these conditions that large amounts of “obesity” patients can be seen all over the world. Therefore prevention and treatment of “abnormal obesity” should be undertaken in childhood, especially for the acute icteric or non-icteric hepatitis pediatric patients, we must tale advantage of effective systemic TCM therapy to avoid the complication of fatty liver. One should aim at early diagnosis and treatment, education of children to develop proper dietary habits and control of children’s body weight within normal range. If the sick child had once been too light or too heavy or showed symptoms of different forms of chronic hepatitis, such as recurring long term nasal hypersensitivity, common cold, bronchitis, asthma, nasal discharge, wetness-heat abdominal pain, paroxysmal diarrhea, menstrual disorders, dysmenorrheal and dermal diseases like acne, eczema and rubella, the possibility of hepatophilic virus infection should be considered. After adolescence, menstrual blood loss in the growing girl should be prevented so that the occurrence of hepatogenic secondary obesity can be avoided. Infantile and childhood hepatoghilic virus disease patients are sufferers of early stage infection; they deserve more attention in prevention and treatment and the effect would be twice while the effort used is half. At present, there are numerous viruses which can cause “liver disease” and the use of blood examination to rule out liver disease or preventive injection of type A, type B hepatitis can not absolutely prevent the occurrence of liver disease; one should be aware of this fact. Now, it is confirmed that not a few fat reducing drugs have anorexia and diarrhea effect and a part of them can also injure the liver and affect the endocrine system of the body. Some of the drugs can cause palpitation, insomnia, anxiety and if severe, may cause renal failure. The patient may have psychotic addiction, and the body weight might decrease rapidly in a short time, but as soon as the drugs are stopped, the body weight would increase by double. Therefore, using drugs to reduce fat is not a clever way.
|
|
| Introduction of cases
Case 1 Huang (code number 541) male, age 60 years. First visit: May, 1997. Thirty years ago, the patient had arthritis which was cured by physicians in a hospital in his country. In the recent ten more years, his right knee joint had repeated pain; he felt tired and had feverish sensation in the chest palms and soles. He had much perspiration and gradually showed generalized edema associated with difficult motivation and loss of libido. He was treated by TCM and WM physicians for 10 more years with no apparent effectiveness. For this reason, he came to Hong Kong and visited our clinic after spending much effort to seek for our location. In May, 1997, physical examination revealed a man of strong build, dark skin color, generalized edema and (++) pitting edema of lower limbs, abdomen distended and full, marked percussion tenderness over hepatic region, intra-abdominal shifting dullness questionable, hepatomegaly at costal margin, no splenomegaly. The symptoms and signs were compatible with the features of chronic hepatitis deficiency of both liver and kidney form. Prescriptions about chronic hepatitis were given to him and he was advised of doing liver function tests at his attending hospital. In August 1997, he visited our clinic for the second time saying that his illness had been relieved after taking 15 parcels of TCM drugs; his knee pain disappeared and his perspiration and dysphonic sensation also decreases and the gastrointestinal system was normal. His body weight had a reduction of 12 pounds. His return visit was delayed because of herpes zoster of the neck and chest which required hospitalization for 18 days. During hospitalization, he had blood examination which revealed type B hepatitis surface antigen and anti-HBC, abnormality of liver function: ALT 82 (normal 5-30), AST 52 (normal 5-30), GGT 60 (normal 5-40), slightly high globulin and abnormal proportion of proteins. Physical examination: good mental status, lessening of facial; edema, more smooth locomotion, abdomen soft but distended, liver normal, (++) pitting edema of lower extremities. He was told to take chronic hepatitis TCM basic formula drugs for one month and have a return visit after this course of treatment. The third return visit was in December 1997, at which time he was feeling well, his appetite and sleeping was normal. He did not feel tired and his libido recovered. The joints did not show any swelling and pain, the stools were regular, hard, one to two times a day. He took the drugs of the preparation Liuwei Dihuang Wan (六味地黃) and the basic formula of hepatitis for two months but now he had stopped the medicine. Physical examination revealed a normal liver, but the lower extremities still showed (++) pitting edema. His was told to time to prevent recurrence. In September 1998, he made a return visit and said that his liver function was entirely normal according to the examination in the local hospital. His daily life was normal, his sexual ability had recovered but some working itching of the skin was still present. Physical examination: revealed a normal liver, but the lower extremities still showed (++) pitting edema. He was told to have supplement of the kidney and take TCM drugs from time to time to prevent recurrence. In September 1998, he made a return visit and said that his liver function was entirely normal according to the examination in the local hospital. His daily life was normal, his sexual ability had recovered but some wondering itching of the skin was still present. Physical examination: puffiness reduced, lower extremities pitting edema (+), generalized sweat stains with scattered hidrotic dermatitis and scratch marks, abdomen soft and distended, liver normal. His was told to take at times TCM drug that could soothe liver, relieve stagnation, clear wetness-heat and supplement kidney water for maintenance of curative effect On 3 July, 2003, he visited our clinic because of hoarseness of voice following common cold. Examination showed a normal liver and (+) edema of lower extremities. His body weight was reduced by 10 kg, after treatment of liver disease and for the time being, he maintained a balanced diet and a steady body weight.
|
|
| By WONG Kwok Hung
Published 26th September 2002 Translated by Professor Zheng in July 2005 |
“Obesity” is an epidemic ! – Comments on hepatogenic secondary obesity (Part II)
| Preface
Hepatogenic secondary obesity is caused by infection of “hepatophilic virus”. “Hepatic edema” and “hepatogenic secondary obesity” are a pair of twins and are the inevitable pathologic processes of human “hepatophilic virus” infection. Hepatic edema is frequently the onset of “secondary obesity”. So, if liver disease is detected early and treated with effective systemic TCM therapy, the development of hepatic edema and obesity can be prevented. In our group of 3000 cases of abnormal margin of liver dullness, nearly 40% have “edema” and “obesity” body figure. If it is mistaken for usual obesity and sought for fat reducing, the result would inevitably be impairment of health and waste of money. |
|
The cause of developing hepatogenic secondary obesity by hepatophhilic virus disease (1) Characteristics of “fatty liver” Acute and chronic hepatophilic virus infection can be complicated by fatty liver and secondary obesity: Clinically, it is a common fact that acute hepatitis patients in the stage of convalescence or chronic hepatitis patients in the active stage may be complicated by “fatty liver”. The latter is characterized by the following:
Besides acute and chronic hepatitis, the clinical causes that may induce fatty liver are hunger, malignant malnutrition (malnutrition due to lack of protein and calorie intake), endocrine disorder (including diabetes, adrenocortical hormones, sex hormones, and acute gestational fatty liver), drug intoxication (including alcohol, tetracycline, carbon tetrachloride, yellow phosphorus); these are closely related to adverse effects on liver metabolism. Behind these factors, is there the existence of hepatophilic virus disease in the patient? This deserves investigation. It is clear that the formation of fatty liver and secondary obesity can not be attributed simply to “over nutrition” or “lack of physical exercise”. Further more, it cannot be treated by “limitation of food” or blindly by “increase of physical exercise” or by administration of “fat reducing drugs”. |
|
| (2) Nervous system damage often occurs after acute or chronic hepatophilic virus infection
Acute a chronic hepatitis can induce nervous system damage, leading to hepatic encephalopathy (肝性腦病), brain edema (腦水腫), meningitis (腦膜炎) and hepatic neuropsychosis (肝性神經精神病); it can also cause chronic hepato-encephalic degeneration, epilepsy and hepatic myelopathy (肝性脊髓病). Some scholars have pointed out statistically that hepatic disease patients with impaired liver function have a 65% incidence or even more of central nervous system damage and in virus hepatitis patients, 70%-80% have encephalic neural symptoms. In fact, some reports have denoted that in the human hypothalamus, these are two nuclei which regulate food intake activity, one is the hypothalamicus ventromedialis nucleus (the satiation centre), the second is ventrolateral hypothalamic nucleus (the hunger centre). Animal experiments showed that if the ventromedialis nucleus was destroyed, the animals increased its food intake and became fat. Clinically, these are some patients with encephalitis and meningitis sequelae who present symptoms of polyphagia and obesity as the chief manifestation. Patients in the acute hepatitis convalescent period and chronic hepatitis active stage often manifest clinically secondary obesity and isn’t this condition related to the damage of hypothalamus by hepatophilic virus? At present, reports about this subject are not seen and this topic should really be investigated. There is no doubt that many infections virus disease such as encephalitis, meningitis and hepatitis can induce “malignant obesity”. So it is clear that there is increasing necessity to have patients diagnosed early and treated early with effective systemic TCM therapy for the complete elimination of toxins and antigen-antibody compounds in the body and for the prevention of edema and secondary obesity.
|
|
| (3) Secondary obesity is usually the result of hepatic edema.
Secondary obesity and hepatic edema may not be easily differentiated in clinical practice. In fact, they interpenetrate one another. Chinese people say: “It is difficult to differentiate fatness and edema”; this virtually denotes the difference between “hepatic edema” and “hepatogenic seconding obesity”. Statistics about patients with “secondary obesity” in our liver disease group showed that in 2925 cases of abnormal margin of liver dullness, physical examination revealed 970 cases of hepatic edema, occupying 33.16% and 191 cases of hepatogenic obesity, accounted for 6.53%. In 1043 male patients, 9% (94 cases) have secondary obesity, but hepatic edema occupied 23.58% (246 cases). In 1882 female patients, only 5.15% (97 cases) have secondary obesity but, in contrast, hepatic edema reached 38.46% (724 cases). It is interesting to find that in secondary obesity male patients are significantly more than female. It is estimated that this is due to a higher incidence of acute hepatitis in male. One the contrary, female patients have a higher incidence of hepatic edema following chronic hepatitis; this is closely related to the physiologic function (menstrual blood loss) characteristic of females. From this, we can see that the possibility of producing hepatic edema and secondary obesity in chronic hepatophilic virus disease patients is high. Liver is the target organ of many important hormones and is also the chief site of degradation, transformation, inter-conversion, storage and excretion of hormones. Liver can synthesize hormone-like substances itself such as sodium excretory factor, angiotensinogen (血管緊張素原) and erthropoietinogen (促紅細胞生成素原), so it can also be regarded as an endocrine organ. Hepatitis is often followed by hepatic dysfunction, leading to disturbance of hormonal metabolism and abnormality of endocrine hormones, e.g. hypothyroidism (甲狀腺機能減低) causing myxedema (粘液性水腫), increase of growth hormone and insulin, hyper-glucagonemia (高胰升血糖素血症) causing hepatogenic diabetes or hypo-glycogenemia (低血糖) in which patients may experience “susceptibility to hunger” and “polyphagia” (多食) the latter conditions tend to produce secondary obesity. In liver disease (especially after the early stage of cirrhosis of liver), there are evidences showing hyper-estrogenemia (高雌激素血症) or male hormone insufficiency where a certain number of male patients with liver disease have feminine breast development and change of body figure to the female type. Some patients may show male sexual hypo-function, which, in childhood, is prone to change the boy into a fat lump, and, besides, the external genitalia may reveal apparent underdevelopment. Therefore, when chronic hepatitis is complicated with other diseases which can induce water and sodium retention, malnutrition, protein deficiency and accumulation of mucous material, the result would be edema, increase of body weight and disfigurement. In addition, in the hepatophilic virus disease patient, there is a gradual increase of concentration of the accumulated “antigen-antibody compounds” as time elapses. Hepatic edema and seconding obesity is produced following the retention of inflammatory fluid in tissue spaces. TCM drugs can eliminate edema and reduce fat; clinical study shows that TCM drugs increase excretion of “antigen-antibody compounds”. Several parcels of TCM drugs can cause shrinkage of liver dullness to normal position and this is a convincing evidence. From the statistical data of TCM from of hepatogenic secondary obesity, we find that the complication of “deficiency of both liver and kidney” accounts for 40% (76/191 cases) which is significantly higher than the usual record 23.6% (692/2934 cases) of the “deficiency of both liver and kidney” form. This indicates that “deficiency of both liver and kidney” is the chief pathological basis of hepatic obesity and it is entirely impossible to obtain fat reduction by the administration of several pills of “fat reducing drug”. So, quite a number of specialists have made the conclusion that majority of the fat reducing projects are not effective. Although the subjects have lowering of body weight, yet their fat figures would reappear in not a long time.
|
|
| (4) Avoid over-dosage or prolonged use of hormones; first choice is effective systemic TCM therapy Over-dosage or prolonged use of hormones is main cause of secondary obesity. Since the appearance of steroids in the world, numerous patients suffering from acute and serious diseases were saved, and because of its outstanding clinical effectiveness, abuse of the drugs by physicians as well as patients had become popular. Aiming at superficial effectiveness but not basic cure, not a few patients indulge at prolonged use of hormones to treat common hepatogenic symptoms and diseases, such as hepatic respiratory treat disease, chronic bronchitis, hepatic pulmonary disease, asthma, gout, various types of dermal diseases, astral malnutrition induced osteoarthritis diseases, lupus erythematosus (紅斑狼瘡) and various allergic diseases, Abuse of steroids may cause retention of water and sodium, full moon face and secondary obesity, so one must be careful in using hormone to treat patients with history of liver disease. For hepatic obesity, it is necessary to treat the fundamental and TCM drugs are more effective in this aspect. If possible, seek for physicians who are able to “treat by syndrome differentiation” and can use the effective systemic TCM therapy as the first choice of therapy without aimless application of hormones.
(5) Acute or chronic blood loss is often the including factor of hepatic obesity Liver participates in many coagulation mechanisms of the human body; besides vitamin K, it can also synthesize fibrinogen and prothrombin (凝血酉每 原). Blood coagulability is impaired when there is hypo-function of the liver. Clinically one may at times encounter purpura (紫癜), epistaxis (鼻衄), hemorrhoidal bleeding and menorrhagia. Especially in females, when they have chronic hepatitis and stagnation of liver qi, they would present symptoms of menstrual irregularity, excessive menstrual blood, deep color menstruation with numerous clots and dysmenorrheal. Excessive loss of blood during menstruation of repeated, prolonged bleeding can result in hemorrhagic anemia. Besides, abnormal clotting of blood after certain hepatogenic diseases may lead to hemorrhage (e.g. peptic ulcer, portal hypertensive gastric disease, biliary hemorrhage, cystic hemorrhage), or large amount of blood loss may occur during operation or delivery. These conditions can lead to hepatic edema and hepatic obesity in the post-convalescence period. In clinical practice, causes of secondary obesity can usually be detected. Therefore, early diagnosis of liver disease and early treatment with TCM drugs and elimination of the opportunity of prolonged loss of blood, early healing of liver disease after a blood loss episode and effective correction of anemia with TCM and western medicine combined method, are the best measures in preventing secondary obesity. |
|
| (6) “Eat less, more physical exercise” is the principle of fat reducing, but mind the “fat reducing pitfall” People usually think that for “over weight” or “obesity”, the management is no other than “eat less” and “do more physical exercise”. Therefore, the conventional use of various food control methods and the aimless increase of physical exercise have become the undoubtedly correct measures of reducing fat. It fact, such popularity conversely let people drop into the “fat reducing pit face”, because hepatic obesity is entirely different from simple obesity. Although the method of reducing calorie in the food control method, despite of not doing physical exercise, can lead to decrease of body weight in a short time, but it can be really effective only if maintained for a long period. But hepatic obesity is a “pathologic type” of obesity, the patient has already nutritional disorder, so that limitation of caloric intake undoubtedly aggravates the liver disease and the result is the complication of acute, sub-acute, or chronic “hepatogenic hypoglycemia” which is induced with certainty at every episode of fasting, meal delay, missed meal time, limited carbohydrate intake or increase of muscular activity. Therefore, due to the longing of reducing fat and the limitation of caloric intake by “eating less” and “doing more physical exercise”, fat in the body is consumed and the individual would have hunger, palpitation, pallor of face, nausea, abdominal pain, intention of defecation, perspiration, tremor of hands or even arrhythmia. Aggravations of the disease may further induce central nervous system symptoms such as vertigo, headache, blurring of vision, sluggish responses or even coma and there is no choice but to stop the fat reducing project. On the other hand, people undergoing fat reduction, for the sake of treating hypoglycemia (低血糖症) or arrhythmia (心律不整) may take more food and the body weight may increase to a level higher than that before fat reducing and, besides, limitation of food blindly may cause “anorexia”(厭食症). All these are “pitfalls of fat reducing”. We should know that once the food intake is limited, the body is inevitably affected in many aspects. The calories provided by fat are four times of carbohydrates, but females going after beauty do not know that fat is very important in the normal development of the body. Some scholars pointed out that without 17% of body weight amount of fat, females would not menstruate, and when the amount is less than 20% of body weight, females can not fertilize or undergo normal delivery. In females, development, pregnancy, delivery, breast feeding, all require an adequate degree of calorie support. If your body weight is above standard but at the same time you are suffering from chronic liver disease, it is certainly a vain hope to reduce fat. It is only when effective systemic TCM therapy is applied to obtain clinical cure of the liver disease, and when the endocrine functions have returned to normal, that the development of a fat body figure can be stopped. On the country, from clinical experience, we find that in the TCM treatment of hepatogenic secondary obesity, if the patient takes a regular diet with high protein nutrients (such as eggs, milk, pork liver and lean meat soup, beef soup, “yin nourishing and kidney supplement” soup), after a condition of “fitness” can be obtained, because enough proteins and amino acid is essential in treatment of hepatoganic malnutrition and anemic and in regulation of colloidal permeability in the body. In addition, hepatic edema may subside more easily and sometimes “keeping fit” may reduce as much as 5-30 lbs of body weight and 3-5 inches of abdominal circumference. But, from the viewpoint of TCM treatment of liver disease, this extra-reward should not be listed as an aim of the therapy.
|
|
| Introduction of cases
Case 2 Lin (code number 2257), male, age 41 years. His mother died 13 years ago from nasopharyngeal cancer (鼻咽癌). He became fat since 16 years of age. Now his height is 1.62m, weight is 81 kg, BMI = 30.86. He complained of pruritus of skin since childhood, especially after perspirations. Repeated pain over left elbow and right knee persisted for ten more years and now he often had swelling of gingivae, aphthae, vague pain over right hypochondrium, fatigue, sleepiness and tiredness and heaviness of lower limbs. Physical examination: tongue enlarged and thick with thin white coating, hepatomegaly of 1.5 cm, (++) edema of lower limbs. The diagnosis was hepatophilic virus disease (herpes, EB virus infection?) with TCM classification of wetness-heat and vaporization, deficiency of both lever and kidney with hepatic osteal malnutrition, hepatic obesity. After TCM therapy, acne was more marked and diarrhea occurred; but after 5 parcels, the liver returned to normal. In the second week of treatment, there was flush of the abdominal skin and also purities and herpes which disappeared after TCM administration. In the 3rd week of treatment, he felt apparent lightness; edema of lower limbs decreased, there was feeling of hunger and the appetite improved. The loosened teeth became stable, the lips turned red and enlargement of the tongue decreased. TCM therapy continued for 6 weeks and medication was stopped after the attainment of clinical cure. The patient was followed up. |
|
|
By WONG Kwok Hung Published on 29th August 2002 Translated by Professor Zheng in January 2005 |
“Obesity” is an epidemic! — Comments on hepatogenic secondary obesity (Part I)
| Preface
In 1997, WHO listed “obesity” as the third chronic killer after smoking and AIDS. Modern people are afraid of “obesity” and become particularly sensitive to the increase of body weight and change of figure. It is especially so in females, and for the purpose of keeping fit, they try by every possible means to “reduce fat”. But what is the result? Most of them ended in disappointment. The chief reason is that the real cause of producing obesity and the correct method of treating it are not found out. The current “obesity epidemic” is spreading over the whole world “Obesity” is an epidemic, this is an undeniable fact, and in many places, numerous statistical data prove this tendency. In the middle of May this year, the annual meeting of WHO issued its newest research material: “Obesity is not only an ‘epidemic’ of developed countries, but also a disease with the acknowledged characteristics of “wealthy society”, spreading to the developing countries. It is estimated that there are about 300 million people suffering from obesity and about 750 million are over weight. In some countries, 30% of the children belong to the fat group and about 22 million children under five years old are overweight or too fat. For example, in Africa, to our surprise, the number of fat children is four times of the undernourished…..”. Statistics in America indicated that from the sixth decade onwards, obesity patients increased by more than a double. The “abnormally fat” population increased from 13% to 22.5% in 1994, and in 1999 to 27%, while the age of the patients becoming younger and younger. In America, there are about 100 million people (97 million adults) over weight or abnormally fat, occupying 55% of the total population. The investigation of North Carolina University in America showed that more than 1/4 of the American population suffered from obesity (male 20%, female 28%). Countries of European Union have 1/3 of their population overweight and there is one obese person in every ten.
From these scattered and incomplete statistical materials, we can still see that “obesity” is really a problem of the whole world. Specialists consider that morbid fatness is an epidemic in the field of public health and the number of victims is up rising. In fact, one would be reluctant to accept that he is fat. Besides, fatness also affects seriously human health. It is unsatisfactory to explain by saying that obesity is simply due to “lack of physical exercise” and to “over nutrition” in modern life or that “the conventional diet habit tends to be substituted by taking high fat instant food or the daily life limited in a small area with insufficient physical exercise”. |
|
|
Differentiate “simply obesity” and “secondary obesity” Hepatogenic secondary “obesity” is due to infection by “hepatophilic virus”. We can not consider obesity as “disease of the rich”. When the calories taken are more than those consumed, the remaining nutritional materials are transformed into fat, which is stored in various tissues and also under the skin and then “obesity” is formed. From the medical point of view, obesity includes “simple obesity” and “secondary obesity”. “Simple obesity” is obesity caused by simple over nutrition. In this kind of obesity, the distribution of fat is even without showing any significant anatomic or formational changes in nervous or endocrine system. Therefore, individuals with mild or moderate obesity usually have their skin delicate and full of luster, abdominal circumference larger but still preserving a loin curvature, umbilicus deeply mined, fat pads protruding around the central umbilicus and curving depression seen at the outer side of sheath of rectus abdominal muscle, causing the fat pad to be more prominent. These individuals have full breasts and buttocks, normal mental condition and good health. The correct method for them to reduce fat is to control food intake adequately, reduce high lipid and glucose diet, do some physical work or exercise and cut down extra-dietary food and calorie intake. Fat reduction method is only effective for simple obesity. “Secondary obesity” is basically different from simple obesity. The main cause, in most patients, is disease in the body leading to accumulation of fat. Secondary obesity is often associated with some other diseases; it may be secondary to certain primary disease in the body and may also be the result of development of certain disease, e.g. hepatogenic obesity (肝源性肥胖), diencephalon obesity (間腦性肥胖), pituitary obesity (垂體性肥胖), (induced by various encephalitis, meningitis, brain injury, brain tumors causing damage to diencephalon and pituitary) sex gland dysfunctional obesity, adrenocortical hyperfunction obesity (腎上腺皮質機能亢進性肥胖), hypothyroidism obesity (甲狀腺機能過低性肥胖), insulin obesity or improper use of drugs (such as abuse of adrenocortical hormones leading to adverse effects like full moon face, sodium retention or prolonged use of sex hormones). The above endocrine disorders all can produce secondary obesity.
|
|
| Mechanism of producing hepatogenic secondary obesity by hepatophilic virus infection
Recent clinical observation reveals that increasing incidence of secondary obesity is found to occur in the acute hepatitis convalescence stage and during chronic active hepatitis. Some cases can be confirmed as “fatty liver” and some are in the stage of “nutritional disorder” produced by metabolic disturbances after infection by “hepatophilic virus” and by prolonged suffering from chronic hepatitis resulting in diseases of various systems. Abnormality of liver function can also cause endocrine disorders which may produce “hepatogenic secondary obesity”. When the human body is infected by hepatophilic virus, the immunologic reaction can cause the liver to develop acute or chronic inflammation. We have mentioned that “hepatophilic virus disease” means that the patient has abnormal margin of hepatic dullness, clinical persistent & repeated, alternating and multiple systemic symptoms of chronic hepatitis and various diseases and complications induced by acute or chronic liver function damage. The disease includes defect in absorption of nutritional material, leading to malnutrition, prolonged anemia, hypoproteinemia (低旦白血症), bleeding from abnormality of clotting mechanism and all these conditions can cause ischemia of pituitary (垂體缺血) and subsequent endocrine disorder. Protective function of the body can lead to over production and retention of adipose tissue which forms hepatic edema, fatty liver and secondary obesity. So, it is doubtless that fatty liver, hepatogenic secondary obesity and hepatic edema are common complications and sequalae of hepatophilic virus disease. In addition, most of the patients with secondary obesity have still a dysfunction liver when first seen by physician. If there is no provision of effective systemic TCM therapy, the chronic hepatitis may persist and gradually complications of heart, blood vessels, apoplexy and diabetes may appear. Obesity can also induce respiratory diseases, muscular and dermal problems, infertility, hypertension and hormone related cancer complications, leading to dysfunction of heart, lung and kidney. Although “abnormal obesity” can induce many complications, but these complications together with “abnormal obesity” are in fact the result of the persistence of chronic “liver disease”.
|
|
|
“Epidemic”— characteristics of hepatogenic secondary obesity
The above mentioned patients may not easily obtain fat reducing results through ordinary fat reducing measures. But the application of “effective systemic TCM therapy” can give clinical cure in chronic hepatitis. Further more, it may be able to correct hepatic edema and hepatic obesity, terminate the progression of chronic hepatitis and make the liver function normal and can eventually avoid the development of complications of obesity.
|
|
| Modern obesity epidemic spreading all over the world
Liver disease is regarded as an infections disease and the fact that induces hepatogenic secondary obesity and that the saying “hepatogenic secondary obesity is epidemic” is not at all irrational. Patients with obesity have increased rapidly in recent years. It is closely related to the recent development of science, frequent communications among people in all corners of the world and the increased chance of hepatophilic virus infection. Data from many places indicate that in the world patients with obesity are increasing every year and their age are becoming younger. If these cases are “hepatogenic secondary obesity”, it indicates that “hepatophilic virus” is silently disseminating in the human community with a high speed. Nowadays, people gradually understand that we must not neglect the harmful effects of “hepatophilic virus” upon human health and the above statement about the cause of hepatogenic edema (or secondary obesity) by chronic hepatitis is an undoubted evidence. The only method to cope with this situation is to take preventive measures at the very beginning, that is to say, detect and treat “chronic hepatophilic virus disease” at an early stage. This is the best way to reduce fat and prevent secondary obesity. It we still use the erroneous old method of reduction of food in take, food preference, or increase exercise blindly, or improper administration of fat reducing drugs, the result will be squander of money or even serious impairment of health.
|
|
| Information about obesity
According to standard body weight, over 10% of standard body weight is regarded as over weight while over 20% of standard body weight is regarded as obesity.
The body mass is measured by the Body Mass Index (“BMI”), i.e. body weight (kg) in proportion to body height (M2): Body Mass Index (BMI) = Body weight (kg)/body height 2 (M2)
Chinese adult standard of obesity Recently, a report was given by Prof. Chou Bei Fan of Epidemic Disease Research Institute, Fou Wai Cardiovascular Disease Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, stated that the Chinese obesity working team, according to the data collected during the ninth decade of 20th century, made an analysis which first suggested a standard of obesity suitable for Chinese adults:
|
|
|
Introduction of cases Case 1 Shu (code number 2612), female, age 32 years. Her first visit was in August 2001, with the complaint of suffering from hemorrhoids two years ago. From time to time, she experienced poor appetite, abdominal pain and distention, constipation, hematochezia and she had an increase of 10 lbs of body weight. She was hospitalized once because of insomnia, palpitation, dim eyesight and vertigo. Her height was 1.57 meter, weight 65 kg, BMI 25.39. Physical examination: marked swelling of lip mucosa, hepatomegaly of 1.5 cm with percussion tenderness, (+) pitting edema over pretibial region. The TCM diagnosis was wetness-heat vaporization, blockage of channels and blood stasis and secondary obesity. After taking 3 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver returned to normal. Through systemic TCM therapy, the body weight reduced to 50 kg, BMI 18.86. She lost about 33 lbs and the abdominal circumference was 73 cm, buttocks circumference reduced from 40 inches to 34 inches. She was now receiving premenstrual TCM therapy. |
|
| By WONG Kwok Hung
Published on 25th July 2002 Translated by Professor Zheng in January 2005 |
Hepatogenic “edema” is not “obesity” (One of the common syndromes of “deficiency of blood and weakness of qi “
| Preface
Not a few people think themselves “obese”, but they do not know in fact it is hepatic edema. Because hepatic edema can cause progressive increase of body weight and body figure, so, often times it is erroneously considered as “obesity”. Actually, many people confuse hepatic edema with “obesity”, and many are misled to adopt incorrect therapeutic measures, for example, abatement of weight can contrarily aggravate edema or even cause “anorexia” which may seriously affect one’s health.
Edema is essentially different from simple obesity. From the TCM point of view the concept that “nine out of ten obese individuals belong to the category of wetness” is extremely correct. Edema is also called water puffiness, it is due to excessive fluid retained in the skin and subcutaneous tissues (including spaces in extra-vascular tissues); weighing the body at regular intervals let one know the degree of edema.
Usually, the appearance of edema of face and mild edema of lower limbs indicates that the body weight has already increased 5%. If edema in these places is marked and pitting edema is present (use the finger to press on the skin over tibial region with persistent mild force, and a pit can be seen when the finger is released) and if the trunk is also edematous, the body weight may have increased about 10%. What are the causes of edema? There are many causes, for example, nutritional, endocrine disease, water and electrolyte imbalance, drug allergy or intoxication. According to the chief causes, one may differentiate, clinically, cardiac edema, hepatic edema, renal edema or nutritional edema. The following is concerned with hepatic edema, our understanding about which offers to the public for the purpose of reference.
|
| Hepatic edema
Hepatic edema is very common but, at the same time, easily neglected by patients and physicians. According to clinical observation, the causes of hepatic edema are many and complicated. The main reason is that in patients with liver disease, the concentration of retained “antigen-antibody compound” in the body increases as time passes by, leading to the accumulation of inflammatory exudates in tissue spaces and subsequently, formation of hepatic edema.
It is not difficult to justify oneself the existence of hepatic edema or not. The following questions may be asked :
The answers to the above questions can tell you whether you have hepatic edema or not. Some people consider themselves “obese” but in fact they are having hepatic edema. Our research centre received 2883 patients with abnormal margin of hepatic dullness in Hong Kong. Among these cases, 952 had various degrees of hepatic edema, occupying 33% (proportion of male to female is 238 : 75) male 23%, female 38.5%. From the statistics, it can be seen that in Hong Kong, where the incidence of liver disease is high, hepatic edema is extremely common. In all of the cases, about 1/3 have various degrees of edema clinically, and in females with abnormal margin of hepatic dullness, about 40% have hepatic edema, significantly higher than the male 23.19%. This is related to the high proportion of deficiency of both qi and blood form in female chronic hepatitis patients and it indicates that hepatic edema is closely related to deficiency of qi and blood and also to anemia.
In the above paragraphs, we have mentioned that hepatophilic virus disease is a disease in which the patient presents abnormality of hepatic dullness, clinical chronic hepatitis conditions showing obstinate, repeated, alternating and multiple systemic symptoms and various diseases induced by acute and chronic damage of liver function. Therefore, it also includes hepatophilic virus infection induced hepatic edema which is caused by “deficiency of qi and weakness of blood”, dysfunction of nutrition and absorption, malnutrition, anemia, hypo-protinemia, endocrine disorders, vitamin deficiency (such as wet beriberi caused by deficiency of vitamin B1).
|
| Severe cases may lead to cirrhosis or carcinoma of liver
In fact, hepatogenic edema, hepatic secondary obesity, and fatty liver all are complications and sequelae of hepatophilic virus disease. It is when the course of chronic hepatitis has entered a comparatively serious stage that hepatic edema would appear clinically. If the condition is not treated by systemic TCM therapy, the degree of edema deepens day by day and it may induce cirrhotic ascites, dysfunction of the heart and lungs or even carcinoma of liver; the latter would often be discovered too late. The former condition is difficult to treat but is still reversible. So, hepatogenic edema is not “obesity” and one should not go after reducing fat blindly.
|
| Abuse of fat reducing drugs damages liver function
From the viewpoint of TCM, “nine out of ten obese individuals suffer from wetness” and this concept is very correct. There is a basic difference between hepatic edema and simple obesity; one must correctly differentiate what is edema and what is obesity. One should not think oneself obese on sheer assumption and take fat reducing measures blindly. If patients with hepatic edema reduce food intake, limit protein ingestion and increase exercise amount which leads to consumption of body energy, or, for the purpose of reducing fat, even take drugs that damage the liver, the hepatic function would be markedly impaired and the liver disease greatly exacerbated.
|
| Drugs should aim at cause of edema
Hepatic edema is not simple obesity caused by over nutrition; it cannot be cured by reducing fat. The edema can be eliminated only by treating the liver disease, that is, by the use of effective TCM therapy. The extended margin of liver dullness can return to normal after several days of treatment and the continuation of therapy can further induce significant regression of edema. We therefore suggest that before taking fat reduction measures, one must make clear that the edema is not caused by liver disease. If hepatophilic virus disease can be detected early and is known to have developed hepatic edema and secondary obesity, TCM and WM therapy should be undertaken in time. In this way, the patient can avoid prolonged suffering from various systemic symptoms of chronic hepatitis and can stop the persistence of edema and secondary obesity and can also keep the body in a healthy condition and prevent progression of the liver disease into cirrhosis or carcinoma.
|
|
Cause of hepatic edema
Chromic virus hepatitis produces hepatic edema caused by attack of infections hepatophilic virus which induces a series of immunologic reactions in the body. Because of disorder of immunologic regulative ability, endotoxemia and microcirculatory dysfunction, the liver cells are damaged liver function is impaired. Abnormal liver function can lead to regression of function of various systems of the body. The causes usually are:
(1) Hepatitis causes symptoms of gastrointestinal disturbance (such as anorexia, nausea, abdominal distention stomache ache, wetness-heat abdominal pain, gastro-intestinal hypersensitivity, constipation, diarrhea). It often affects the patient’s appetite and nutritional absorption. So, in chronic hepatitis, edema due to malnutrition is frequently encountered.
(2) Defect in protein synthesis (especially in albumin synthesis): Although the daily protein intake and absorption is normal, but if there is decreased synthetic ability of protein in the liver, the plasma albumin level would be low and also the plasma colloidal permeability is lowered so that mal-nutritional edema is likely to occur. (Lowering of plasma albumin is of diagnostic value, and 2.5% is considered as marginal level. In severe edema, the plasma albumin is usually below 2 g %).
(3) Hepatic coagulopathy: Liver participates with many coagulative functions of the body; besides vitamin K, it can also synthesize fibrinogen and thrombin. Decrease of hepatic function can affect the coagulation of blood and is likely to cause various kinds of acute or chronic bleeding. Clinically, the conditions often seen are subcutaneous ecchymosis (皮下瘀斑), hematochezia, epistaxis, hemorrhoidal bleeding, and, especially in female chronic hepatitis patients, irregular menstruation, menorrhagia, prolonged bleeding periods, dark color blood with numerous blood clots and repeated dysmenorrhea. During delivery, the bleeding is profuse and in operation or trauma, the blood loss is particularly excessive. Edema caused by repeated and prolonged chronic blood loss is a fact frequently encountered.
(4) Endocrine disorder: Liver is the target organ of many important hormones and is also the main site of hormone degradation, interchange, transformation, storage and excretion. Liver can synthesize sodium excretion factor, angiotensinogen (血管緊張素原) and erythropoietinogen (促紅細胞生成素原) and therefore it is also an endocrine organ. So, in hepatitis, hormonal disturbance is frequently induced, for example, hypothyroidism leads to myxedema (粘液水腫) and also, there may exist a rise of growth hormone and insulin. Pancreatic glucagonemia causes hepatogenic diabetes or hypoglycemia. At this time, the patient tends to be hungry easily and eat too much with the result of developing secondary obesity. Hyperestrogenemia and decrease of male hormone can be frequently seen in hepatic disease. A small number of male patients have breast development and feminine figure. If there is decrease of male sexual function in childhood, the patient tends to become fat and the external genital organ would also show significant underdevelopment.
(5) Abuse of hormones : The patient, because of long term extra-hepatic complications (such as asthma, german measles, eczema, osteal arthritic diseases like gout or erythematosus) used drugs like corticosteroids or sex hormones improperly (such as in treatment of infertility). In addition, before or after climacteric in male or female, it can also cause, in a short time, retention of water and sodium and subsequently induces edema, obesity and significant increase of body weight.
(6) Deficiency of B group vitamins: When there is dysfunction of liver, the patient’s thiamine acidifying ability decrease, the usage of vitamins B1 is interfered, the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic acid is impaired, so that the oxygenation process of glucose is affected. Further more, it affects the energy supply of nerve cells, leading to accumulation of pyruvic acid lactic acid in nerve tissues and subsequently, to multiple peripheral neuritis (多發性周圍神經炎) and wet beriberi (濕性腳氣) which produces edema.
In addition, some drugs may damage the liver and electrical therapy or chemotherapy may impair liver function and in such conditions, the patient’s edema may be aggravated. In clinical practice, it is often observed that long term administration of diuretics does not show marked effect in elimination of edema, but when TCM therapy is used, the edema regresses significantly or even completely disappears.
|
| Introduction of cases
Case 1 Run (code number 2027) female, age 32 years. First visit: December 1999. She complained of suffering from acute nephritis when she was 10 years old and it was finally cured. In the recent 5 years, she had edema which was more masked in the lower limbs. She received repeated TCM and WH treatment with no effectiveness. She had many times of physical examination and laboratory examination which ruled out cardiac and renal edema. Some physicians diagnosed it as endocrine disorder, but still the cause of edema was not clarified. At the onset of edema, she felt distensive pain in the lower limbs and afterwards, for a long period, she experienced tiredness, dreamfulness, poor sleeping, headache, abdominal distention, constipation and her body weight increased from 110 lbs to 130 lbs. She had irregular menstruation the amount of which was large with many blood clots and she occasionally had dysmenorrhea.
Physical examination: fissured tongue with red tip, medial furrow and white coating, face flushing, abdomen depressed without ascites, shrinkage of area of percussion dullness, liver lower margin 4.5 cm. above costal margin (3 finger breath above coastal margin), lower limbs with (+++) pitting edema more marked over dorsal surface of both feet, the latter showing extremely thin dorsal skin with transparency. (She brought her 1997 blood and urine examination reports, liver and spleen computer scan, chest and reprography x-ray film, but these did not reveal any abnormality ).
After taking 3 parcels of TCM drugs, shrinkage of liver dullness disappeared and through percussion the liver was actually enlarged to 1.5 cm with percussion tenderness. Another 4 parcels were taken and the liver was normal. She was treated afterwards by systemic TCM therapy and the edema gradually subsided, the clinical symptoms disappeared. She received TCM therapy for about 3 months and the edema of the lower limbs disappeared completely. Treatment was stopped after clinical cure and the patient was followed up.
|
| Case 2
Chan (code number 2832) female, age 67 years. Her first visit was on March 26, 2002 with the complaint of repeated abnormal sensation of lower limbs which included numbness, soreness, formication (蟻走感), burning heat sensation and paroxysmal pain of right gastronomies muscle. The latter condition caused persistent pain for two months with functional disability two years ago. Now the pain persisted for two more weeks and severe calf pain and fatigue attacked her for several days. Physical examination: haggard, puffy, flushing of face, tongue enlarged, lower limbs edema (+++), gastrocnemius muscle no significant tenderness, abdomen soft and distended, hepatomegaly of 1.5 cm.
After taking two parcels of TCM drugs, she had diarrhea, bowel movements 3 times in one hour amount large and stinking. When 3 parcels had been taken, edema of the lower limbs nearly disappeared and pitting edema was (+). The tongue was still enlarged but the liver was normal. Another week of TCM treatment gave her no pain in walking. In the course of treatment, she had occasional insomnia, fatigue, headache, acid regurgitation, stomache distention after meal and drawing pain of the diseased leg in walking. When going upstairs, pain was felt over the right gastroenemius muscle and in the third week of treatment, the right angle of lips showed vesicular eruptions. The symptoms disappeared when TCM treatment was going on. After 6 weeks of systemic TCM therapy, clinical cure was obtained and treatment was stopped for observation.
|
| Case 3
Yang (code number 2769) male, age 45 years. First visit: January, 2002. He complained of being a carrier of type B hepatitis virus for ten more years and he had a history of asthma in childhood. Twenty years ago, he had gastric hemorrhage and now he still felt upper abdominal distention and belching whether hungry or full. Gastroscopy revealed no abnormality. In recent years, he often experienced photophobia, dermal pruritus, fatigue, edema of lower limbs and early whiteness of hair which was dyed.
Physical examination: skin color dark, puffy, lips edematous with fissuring, After taking 3 parcels of TCM drugs, gastric discomfort was relieved; belching and flatulence stopped and the liver was normal. During the administration of TCM drugs, he experienced dryness of eyes, fatigue, sleepiness, dreamfulness, yellowish urine with foam, repeated belching, occasional diarrhea and pain of hypochondria (脅痛); edema of lower limbs disappeared. A total of 42 parcels of TCM drugs were taken, at the end of which clinical cure was attained. After that, he was followed up.
|
| Case 4
Lin (code number 2341) female, age 63 years. She first visited the clinic in January 2001 with the complaint of having fatigue, discomfort of heart, shortness of breath, itching of throat, coughing, shoulder and loin pain and insomnia for ten more years. Repeated drug treatment was not effective. She received hysterectomy (子宮切除) because of uterine myoma (宮肌瘤) ten more years ago.
Physical examination: puffy, skin palish yellow, tongue enlarged with medial fissure, tympanitic frog like abdomen, hepatomegaly of 1.5 cm, percussion tenderness over hepatic region, edema of lower extremities, pretibial pitting edema (+).
After taking 3 parcels of TCM drugs, the liver returned to normal. Her sleeping could last for five hours, but she still had mild vertigo and shortness of breath. One week later, the edema improved and fatigue disappeared. She had some itching of throat, occasional cough with abundant sputum and her sleeping was good. Mild vertigo occurred after waking up in the morning. She had bowel movement once in several days; the stools were hard. Blood pressure: 110/70 mmHg. The tongue was enlarged and liver normal. Edema of lower extremities disappeared. For the treatment of shoulder and loin pain caused by hepatic osteal malnutrition, she was given TCM therapy for nearly three months.
|
| By WONG Kwok Hung
Published on 20th June 2002 Translated by Professor Zheng in December 2004 |