Hepatitis means inflammation of the humane liver; the condition may be severe, mild, acute or chronic. There are various causes, such as infection by virus or bacteria, or due to drugs, alcohol and toxic substances, acute and chronic hepatitis caused by virus are the most common types, usually called “virus hepatitis”. At the present time, it should be considered the most serious disease that affects humane health. The route of infection of virus hepatitis is varied. The virus can infect other people through food and drinking, blood, body fluid, sexual contact and the maternal fatal pathway.
According to the type of virus, virus hepatitis can be classified as A, B, C, D, E five forms, recently new forms have been discovered and are called hepatitis F and G. The most common form is hepatitis B and according to a survey by WHO in 1998, about 2 billion people in the world have been infected by hepatitis B virus, hepatitis B virus carriers amounted to more than 300 million in which 73% were Asians. Every year, more than 200 million people die from hepatitis B. In China, hepatitis B virus carriers amounted to 120 million, occupying one tenth of the population of the country and in these people about 30 million progress into chronic hepatitis. Annually, about 300 thousand people die from liver disease in which virus hepatitis ranges first in incidence rate and mortality rate. The condition in Hong Kong is not exceptional; data from the Health Department in 1999 shows hepatitis B virus carriers amount to one tenth of the population, one quarter of which might progress into cirrhosis of liver, or carcinoma and carcinoma of liver ranges second in malignant tumors in Hong Kong. In fact, the above data reveals only a small part of the whole condition; the actual situation is certainly much more serious.
Why early chronic hepatitis cannot be detected earlier?
The change of chronic hepatitis to sclesossis of liver and hepatic carcinoma undergoes a rather long period but why early chronic hepatitis cannot be diagnosed early? There are three important causes.
(1) The symptoms of early chronic hepatitis are not marked and many early hepatitis symptoms are often erroneous diagnosed as common disease of other systems and discovered only when the course of illness has advanced.
(2) Clinical diagnosis relies too much on scientific parameters such as blood examination, ultrasound, computer scanning, etc. In fact, blood examinations may present false negative results and ultrasound has limited effect to medium tissues. Clinicians relying only upon the result of accessory examinations will often misdiagnose disease or let diagnoses missed. Patients endure high costs of examinations and drugs but get the false information that their conditions are “satisfactory”. When a patient complains his condition is aggravating, it is altogether too late.
(3) Virus hepatitis is definitely not limited to the present seven forms. Therefore, relying upon blood examinations, ultrasound and computer scanning alone to diagnose hepatitis A, B, C often leads to erroneous diagnosis and treatment of many virus hepatitis patients.
Recognize hepatophilic virus
There are numerous viruses that can cause hepatitis; some viruses, after invading the human body, have affinity for the liver and their common characteristic is “hepatophilic virus” and similarly, they can produce pathological changes and symptoms of hepatitis, for example, the cytomegalovirus, EB virus, yellow fever virus, rubella virus, Coxsackie virus, herpes simplex virus, etc. Therefore, virus that causes virus hepatitis is called hepatophilic virus and the former concept that virus hepatitis must be infected by hepatitis virus is no longer completely correct.
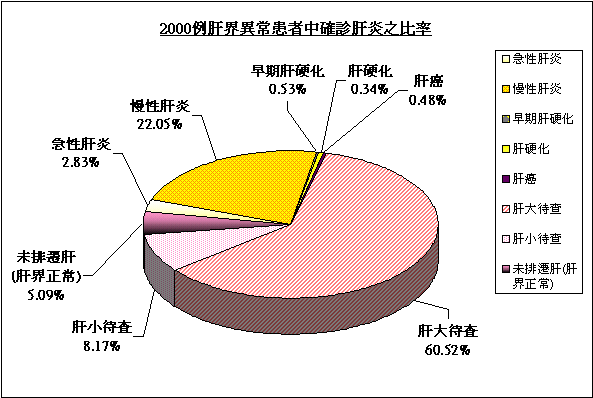
In fact, an important point in diagnosing chronic hepatitis is the primary physical examination, through which one can understand the hepatic and splenic dullness normal or not. This is an indispensable step with extremely high preciseness and clinicians depend upon it to check the diagnosis and also effectiveness of drugs and observe the result in reference to the clinical criteria. From 2000 patients with abnormal liver dullness in Hong Kong (figure 1), we discover about 70% of the cases, according to the present diagnostic criteria, can not be diagnosed as chronic hepatitis. Therefore, we consider the necessity of raising the concept of “hepatophilic virus” infection and call it “hepatophilic virus disease” which is differentiated from the narrow sense of chronic virus hepatitis.
In the special column “Talks about hepatitis from elderly physicians” we shall systematically investigate the general status of chronic hepatitis and renew the following recognization“ First, Hepatophlic virus is the source of many disease”. Second, traditional Chinese medical treatment of hepatophilic virus diseases is the most effective method at the present time. Acceptance of the diagnosis of “hepatophilic virus disease” makes possible further improvement of the treatment and prevention of chronic hepatitis and patients suffering from this disease may then be able to receive timely diagnosis and treatment.
By WONG Kwok Hung
5th September 2000
(Translated by Professor ZHENG Hua En)
